| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
From the moment we are born until the moment we die, we continue to develop.
As discussed at the beginning of this chapter, developmental psychologists often divide our development into three areas: physical development, cognitive development, and psychosocial development. Mirroring Erikson’s stages, lifespan development is divided into different stages that are based on age. We will discuss prenatal, infant, child, adolescent, and adult development.
How did you come to be who you are? From beginning as a one-cell structure to your birth, your prenatal development occurred in an orderly and delicate sequence.
There are three stages of prenatal development: germinal, embryonic, and fetal. Let’s take a look at what happens to the developing baby in each of these stages.
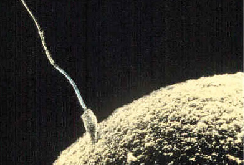
In the discussion of biopsychology earlier in the book, you learned about genetics and DNA. A mother and father’s DNA is passed on to the child at the moment of conception. Conception occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg and forms a zygote ( [link] ). A zygote begins as a one-cell structure that is created when a sperm and egg merge. The genetic makeup and sex of the baby are set at this point. During the first week after conception, the zygote divides and multiplies, going from a one-cell structure to two cells, then four cells, then eight cells, and so on. This process of cell division is called mitosis . Mitosis is a fragile process, and fewer than one-half of all zygotes survive beyond the first two weeks (Hall, 2004). After 5 days of mitosis there are 100 cells, and after 9 months there are billions of cells. As the cells divide, they become more specialized, forming different organs and body parts. In the germinal stage, the mass of cells has yet to attach itself to the lining of the mother’s uterus. Once it does, the next stage begins.
After the zygote divides for about 7–10 days and has 150 cells, it travels down the fallopian tubes and implants itself in the lining of the uterus. Upon implantation, this multi-cellular organism is called an embryo . Now blood vessels grow, forming the placenta. The placenta is a structure connected to the uterus that provides nourishment and oxygen from the mother to the developing embryo via the umbilical cord. Basic structures of the embryo start to develop into areas that will become the head, chest, and abdomen. During the embryonic stage, the heart begins to beat and organs form and begin to function. The neural tube forms along the back of the embryo, developing into the spinal cord and brain.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?