| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
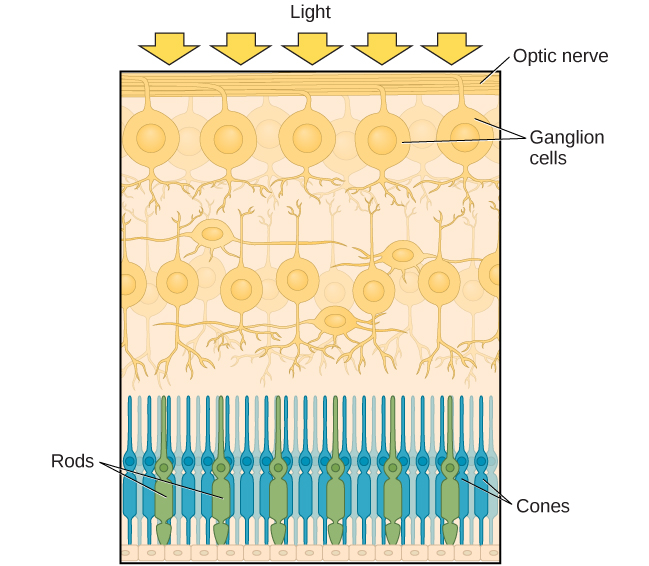
We have all experienced the different sensitivities of rods and cones when making the transition from a brightly lit environment to a dimly lit environment. Imagine going to see a blockbuster movie on a clear summer day. As you walk from the brightly lit lobby into the dark theater, you notice that you immediately have difficulty seeing much of anything. After a few minutes, you begin to adjust to the darkness and can see the interior of the theater. In the bright environment, your vision was dominated primarily by cone activity. As you move to the dark environment, rod activity dominates, but there is a delay in transitioning between the phases. If your rods do not transform light into nerve impulses as easily and efficiently as they should, you will have difficulty seeing in dim light, a condition known as night blindness.
Rods and cones are connected (via several interneurons) to retinal ganglion cells. Axons from the retinal ganglion cells converge and exit through the back of the eye to form the optic nerve . The optic nerve carries visual information from the retina to the brain. There is a point in the visual field called the blind spot : Even when light from a small object is focused on the blind spot, we do not see it. We are not consciously aware of our blind spots for two reasons: First, each eye gets a slightly different view of the visual field; therefore, the blind spots do not overlap. Second, our visual system fills in the blind spot so that although we cannot respond to visual information that occurs in that portion of the visual field, we are also not aware that information is missing.
The optic nerve from each eye merges just below the brain at a point called the optic chiasm . As [link] shows, the optic chiasm is an X-shaped structure that sits just below the cerebral cortex at the front of the brain. At the point of the optic chiasm, information from the right visual field (which comes from both eyes) is sent to the left side of the brain, and information from the left visual field is sent to the right side of the brain.
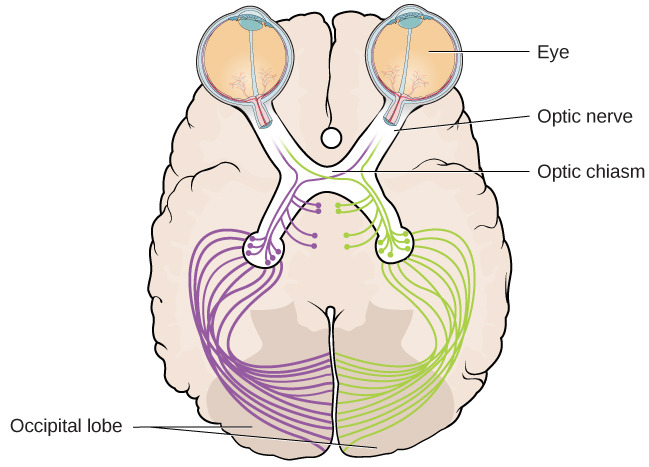
Once inside the brain, visual information is sent via a number of structures to the occipital lobe at the back of the brain for processing. Visual information might be processed in parallel pathways which can generally be described as the “what pathway” and the “where/how” pathway. The “what pathway” is involved in object recognition and identification, while the “where/how pathway” is involved with location in space and how one might interact with a particular visual stimulus (Milner&Goodale, 2008; Ungerleider&Haxby, 1994). For example, when you see a ball rolling down the street, the “what pathway” identifies what the object is, and the “where/how pathway” identifies its location or movement in space.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?