| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Personality refers to the long-standing traits and patterns that propel individuals to consistently think, feel, and behave in specific ways. Our personality is what makes us unique individuals. Each person has an idiosyncratic pattern of enduring, long-term characteristics and a manner in which he or she interacts with other individuals and the world around them. Our personalities are thought to be long term, stable, and not easily changed. The word personality comes from the Latin word persona . In the ancient world, a persona was a mask worn by an actor. While we tend to think of a mask as being worn to conceal one’s identity, the theatrical mask was originally used to either represent or project a specific personality trait of a character ( [link] ).

The concept of personality has been studied for at least 2,000 years, beginning with Hippocrates in 370 BCE (Fazeli, 2012). Hippocrates theorized that personality traits and human behaviors are based on four separate temperaments associated with four fluids (“humors”) of the body: choleric temperament (yellow bile from the liver), melancholic temperament (black bile from the kidneys), sanguine temperament (red blood from the heart), and phlegmatic temperament (white phlegm from the lungs) (Clark&Watson, 2008; Eysenck&Eysenck, 1985; Lecci&Magnavita, 2013; Noga, 2007). Centuries later, the influential Greek physician and philosopher Galen built on Hippocrates’s theory, suggesting that both diseases and personality differences could be explained by imbalances in the humors and that each person exhibits one of the four temperaments. For example, the choleric person is passionate, ambitious, and bold; the melancholic person is reserved, anxious, and unhappy; the sanguine person is joyful, eager, and optimistic; and the phlegmatic person is calm, reliable, and thoughtful (Clark&Watson, 2008; Stelmack&Stalikas, 1991). Galen’s theory was prevalent for over 1,000 years and continued to be popular through the Middle Ages.
In 1780, Franz Gall, a German physician, proposed that the distances between bumps on the skull reveal a person’s personality traits, character, and mental abilities ( [link] ). According to Gall, measuring these distances revealed the sizes of the brain areas underneath, providing information that could be used to determine whether a person was friendly, prideful, murderous, kind, good with languages, and so on. Initially, phrenology was very popular; however, it was soon discredited for lack of empirical support and has long been relegated to the status of pseudoscience (Fancher, 1979).

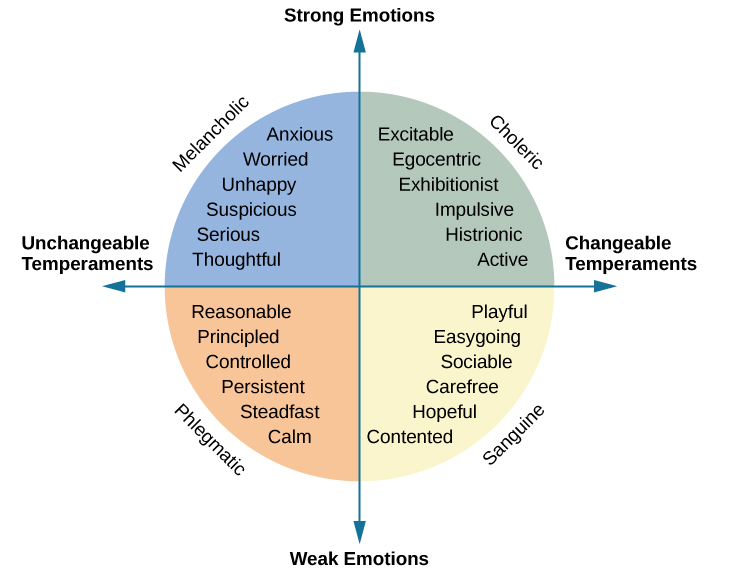
In the centuries after Galen, other researchers contributed to the development of his four primary temperament types, most prominently Immanuel Kant (in the 18th century) and psychologist Wilhelm Wundt (in the 19th century) (Eysenck, 2009; Stelmack&Stalikas, 1991; Wundt, 1874/1886) ( [link] ). Kant agreed with Galen that everyone could be sorted into one of the four temperaments and that there was no overlap between the four categories (Eysenck, 2009). He developed a list of traits that could be used to describe the personality of a person from each of the four temperaments. However, Wundt suggested that a better description of personality could be achieved using two major axes: emotional/nonemotional and changeable/unchangeable. The first axis separated strong from weak emotions (the melancholic and choleric temperaments from the phlegmatic and sanguine). The second axis divided the changeable temperaments (choleric and sanguine) from the unchangeable ones (melancholic and phlegmatic) (Eysenck, 2009).
Sigmund Freud’s psychodynamic perspective of personality was the first comprehensive theory of personality, explaining a wide variety of both normal and abnormal behaviors. According to Freud, unconscious drives influenced by sex and aggression, along with childhood sexuality, are the forces that influence our personality. Freud attracted many followers who modified his ideas to create new theories about personality. These theorists, referred to as neo-Freudians, generally agreed with Freud that childhood experiences matter, but they reduced the emphasis on sex and focused more on the social environment and effects of culture on personality. The perspective of personality proposed by Freud and his followers was the dominant theory of personality for the first half of the 20th century.
Other major theories then emerged, including the learning, humanistic, biological, evolutionary, trait, and cultural perspectives. In this chapter, we will explore these various perspectives on personality in depth.
View this video for a brief overview of some of the psychological perspectives on personality.
Personality has been studied for over 2,000 years, beginning with Hippocrates. More recent theories of personality have been proposed, including Freud’s psychodynamic perspective, which holds that personality is formed through early childhood experiences. Other perspectives then emerged in reaction to the psychodynamic perspective, including the learning, humanistic, biological, trait, and cultural perspectives.
How would you describe your own personality? Do you think that friends and family would describe you in much the same way? Why or why not?
How would you describe your personality in an online dating profile?
What are some of your positive and negative personality qualities? How do you think these qualities will affect your choice of career?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?