| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To derive the equation of an ellipse centered at the origin, we begin with the foci and The ellipse is the set of all points such that the sum of the distances from to the foci is constant, as shown in [link] .
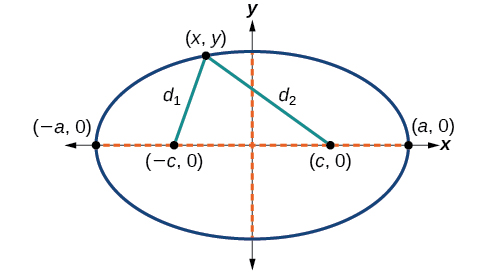
If is a vertex of the ellipse, the distance from to is The distance from to is . The sum of the distances from the foci to the vertex is
If is a point on the ellipse, then we can define the following variables:
By the definition of an ellipse, is constant for any point on the ellipse. We know that the sum of these distances is for the vertex It follows that for any point on the ellipse. We will begin the derivation by applying the distance formula. The rest of the derivation is algebraic.
Thus, the standard equation of an ellipse is This equation defines an ellipse centered at the origin. If the ellipse is stretched further in the horizontal direction, and if the ellipse is stretched further in the vertical direction.
Standard forms of equations tell us about key features of graphs. Take a moment to recall some of the standard forms of equations we’ve worked with in the past: linear, quadratic, cubic, exponential, logarithmic, and so on. By learning to interpret standard forms of equations, we are bridging the relationship between algebraic and geometric representations of mathematical phenomena.
The key features of the ellipse are its center, vertices , co-vertices , foci , and lengths and positions of the major and minor axes . Just as with other equations, we can identify all of these features just by looking at the standard form of the equation. There are four variations of the standard form of the ellipse. These variations are categorized first by the location of the center (the origin or not the origin), and then by the position (horizontal or vertical). Each is presented along with a description of how the parts of the equation relate to the graph. Interpreting these parts allows us to form a mental picture of the ellipse.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?