| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given a rational function, sketch a graph.
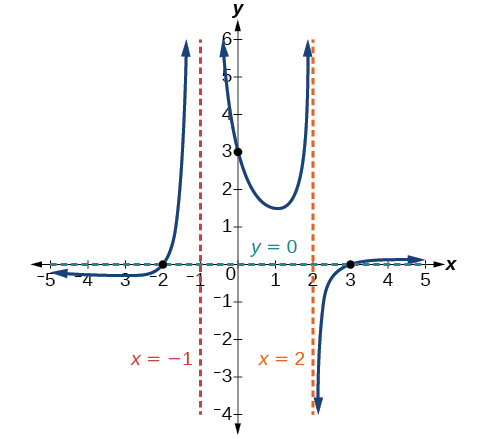
Sketch a graph of
We can start by noting that the function is already factored, saving us a step.
Next, we will find the intercepts. Evaluating the function at zero gives the y -intercept:
To find the x -intercepts, we determine when the numerator of the function is zero. Setting each factor equal to zero, we find x -intercepts at and At each, the behavior will be linear (multiplicity 1), with the graph passing through the intercept.
We have a y -intercept at and x -intercepts at and
To find the vertical asymptotes, we determine when the denominator is equal to zero. This occurs when and when giving us vertical asymptotes at and
There are no common factors in the numerator and denominator. This means there are no removable discontinuities.
Finally, the degree of denominator is larger than the degree of the numerator, telling us this graph has a horizontal asymptote at
To sketch the graph, we might start by plotting the three intercepts. Since the graph has no x -intercepts between the vertical asymptotes, and the y -intercept is positive, we know the function must remain positive between the asymptotes, letting us fill in the middle portion of the graph as shown in [link] .

The factor associated with the vertical asymptote at was squared, so we know the behavior will be the same on both sides of the asymptote. The graph heads toward positive infinity as the inputs approach the asymptote on the right, so the graph will head toward positive infinity on the left as well.
For the vertical asymptote at the factor was not squared, so the graph will have opposite behavior on either side of the asymptote. See [link] . After passing through the x -intercepts, the graph will then level off toward an output of zero, as indicated by the horizontal asymptote.
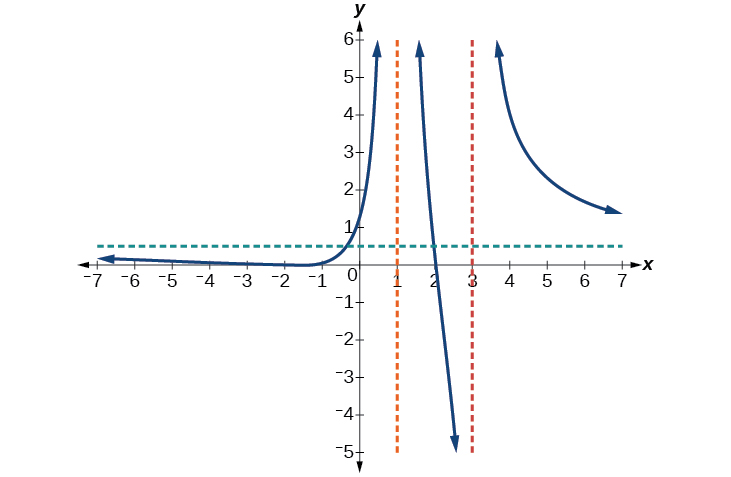
Given the function use the characteristics of polynomials and rational functions to describe its behavior and sketch the function.
Horizontal asymptote at Vertical asymptotes at y -intercept at
x -intercepts at is a zero with multiplicity 2, and the graph bounces off the x -axis at this point. is a single zero and the graph crosses the axis at this point.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?