| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One of the invaluable applications of the determination of viscosity is identifying a given liquid as Newtonian or non-Newtonian in nature.
Moreover, non-Newtonian liquids can be further subdivided into classes by their viscous behavior with shear stress:
Viscometers are used to measure viscosity. There are seven different classes of viscometer:
Capillary viscometers are the most widely used viscometers when working with Newtonian fluids and measure the flow rate through a narrow, usually glass tube. In some capillary viscometers, an external force is required to move the liquid through the capillary; in this case, the pressure difference across the length of the capillary is used to obtain the viscosity coefficient.
Capillary viscometers require a liquid reservoir, a capillary of known dimensions, a pressure controller, a flow meter, and a thermostat be present. These viscometers include, Modified Ostwald viscometers, Suspended-level viscometers, and Reverse-flow viscometers and measure kinematic viscosity.
The equation governing this type of viscometry is the Pouisille law ( [link] ), where Q is the overall flowrate, ΔP, the pressure difference, a , the internal radius of the tube, η, the dynamic viscosity, and l the path length of the fluid.
Here, Q is equal to V/t; the volume of the liquid measured over the course of the experiment divided by the time required for it to move through the capillary where V is volume and t is time.
For gravity-type capillary viscometers, those relying on gravity to move the liquid through the tube rather than an applied force, [link] is used to find viscosity, obtained by substituting the relation [link] with the experimental values, where P is pressure, ρ is density, g is the gravitational constant, and h is the height of the column.
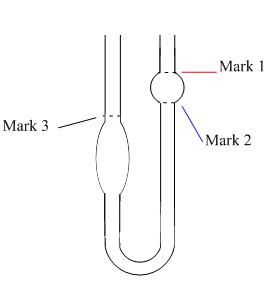
An example of a capillary viscometer (Ostwald viscometer) is shown in [link] .
Commonly found in the oil industry, orifice viscometers consist of a reservoir, an orifice, and a receiver. These viscometers report viscosity in units of efflux time as the measurement consists of measuring the time it takes for a given liquid to travel from the orifice to the receiver. These instruments are not accurate as the set-up does not ensure that the pressure on the liquid remains constant and there is energy lost to friction at the orifice. The most common types of these viscometer include Redwood, Engler, Saybolt, and Ford cup viscometers. A Saybolt viscometer is represented in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?