| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visually inspect the sample as it heats. Once melting begins, note the temperature. When the sample is completely melted, note the temperature again. That is the melting point range for the sample. Pure samples typically have a 1 - 2 °C melting point range, however, this may be broadened due to colligative properties.
There are two primary uses of melting point analysis data. The first is for qualitative identification of the sample, and the second is for quantitative purity characterization of the sample.
For identification, compare the experimental melting point range of the unknown to literature values. There are several vast databases of these values. Obtain a pure sample of the suspected chemical and mix a small amount of the unknown with it and conduct melting point analysis again. If a sharp melting point range is observed at similar temperatures to the literature values, then the unknown has likely been identified correctly. Conversely, if the melting point range is depressed or broadened, which would be due to colligative properties, then the unknown was not successfully identified.
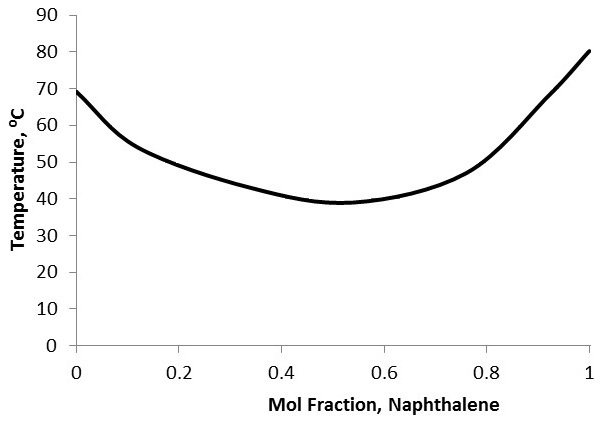
To characterize purity, first the identity of the solvent (the main constituent of the sample) and the identity of the primary solute need to be known. This may be done using other forms of analysis, such as gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy coupled with a database. Because melting point depression is unique between chemicals, a mixed melting curve comparing molar fractions of the two constituents with melting point needs to either be obtained or prepared ( [link] ). Simply prepare standards with known molar fraction ratios, then perform melting point analysis on each standard and plot the results. Compare the melting point range of the experimental sample to the curve to identify the approximate molar fractions of the constituents. This sort of purity characterization cannot be performed if there are more than two primary components to the sample.
Melting point analysis is fairly specific and accurate given its simplicity. Because melting point is a unique physical characteristic of a substance, melting point analysis does have high specificity. Although, many substances have similar melting points, so having an idea of possible chemicals in mind can greatly narrow down the choices. The thermometers used are also accurate. However, melting point is dependent on pressure as well, so experimental results can vary from literature values, especially at extreme locations, i.e., places of high altitude. The biggest source of error stems from the visual detection of melting by the experimenter. Controlling the change rate and running multiple trials can lessen the degree of error introduced at this step.
Melting point analysis is a quick, relatively easy, and inexpensive preliminary analysis if the sample is already mostly pure and has a suspected identity. Additionally, analysis requires small samples only.
As with any analysis, there are certain drawbacks to melting point analysis. If the sample is not solid, melting point analysis cannot be done. Also, analysis is destructive of the sample. For qualitative identification analysis, there are now more specific and accurate analyses that exist, although they are typically much more expensive. Also, samples with more than one solute cannot be analyzed quantitatively for purity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?