| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In any sort of discussion of crystalline materials, it is useful to begin with a discussion of crystallography: the study of the formation, structure, and properties of crystals. A crystal structure is defined as the particular repeating arrangement of atoms (molecules or ions) throughout a crystal. Structure refers to the internal arrangement of particles and not the external appearance of the crystal. However, these are not entirely independent since the external appearance of a crystal is often related to the internal arrangement. For example, crystals of cubic rock salt (NaCl) are physically cubic in appearance. Only a few of the possible crystal structures are of concern with respect to simple inorganic salts and these will be discussed in detail, however, it is important to understand the nomenclature of crystallography.
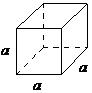
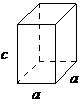
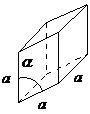
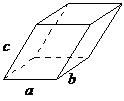
The Bravais lattice is the basic building block from which all crystals can be constructed. The concept originated as a topological problem of finding the number of different ways to arrange points in space where each point would have an identical “atmosphere”. That is each point would be surrounded by an identical set of points as any other point, so that all points would be indistinguishable from each other. Mathematician Auguste Bravais discovered that there were 14 different collections of the groups of points, which are known as Bravais lattices. These lattices fall into seven different "crystal systems”, as differentiated by the relationship between the angles between sides of the “unit cell” and the distance between points in the unit cell. The unit cell is the smallest group of atoms, ions or molecules that, when repeated at regular intervals in three dimensions, will produce the lattice of a crystal system. The “lattice parameter” is the length between two points on the corners of a unit cell. Each of the various lattice parameters are designated by the letters a , b , and c . If two sides are equal, such as in a tetragonal lattice, then the lengths of the two lattice parameters are designated a and c , with b omitted. The angles are designated by the Greek letters α, β, and , such that an angle with a specific Greek letter is not subtended by the axis with its Roman equivalent. For example, α is the included angle between the b and c axis.
[link] shows the various crystal systems, while [link] shows the 14 Bravais lattices. It is important to distinguish the characteristics of each of the individual systems. An example of a material that takes on each of the Bravais lattices is shown in [link] .
| System | Axial lengths and angles | Unit cell geometry |
| cubic | a = b = c, α = β = = 90° |
 |
| tetragonal | a = b ≠ c, α = β = = 90° |
 |
| orthorhombic | a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = = 90° |
 |
| rhombohedral | a = b = c, α = β = ≠ 90° |
 |
| hexagonal | a = b ≠ c, α = β = 90°, = 120° |
 |
| monoclinic | a ≠ b ≠ c, α = = 90°, β ≠ 90° |
 |
| triclinic | a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ |
 |

| Crystal system | Example |
| triclinic | K 2 S 2 O 8 |
| monoclinic | As 4 S 4 , KNO 2 |
| rhombohedral | Hg, Sb |
| hexagonal | Zn, Co, NiAs |
| orthorhombic | Ga, Fe 3 C |
| tetragonal | In, TiO 2 |
| cubic | Au, Si, NaCl |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?