| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One problem with this classical formulation is that it is not general. We cannot use it, for example, to describe vibrations of diatomic molecules, where quantum effects are important. A first step toward a quantum formulation is to use the classical expression to limit mention of a “spring” constant between the atoms. In this way the potential energy function can be written in a more general form,
Combining this expression with the time-independent Schrӧdinger equation gives
To solve [link] —that is, to find the allowed energies E and their corresponding wave functions —we require the wave functions to be symmetric about (the bottom of the potential well) and to be normalizable. These conditions ensure that the probability density must be finite when integrated over the entire range of x from to . How to solve [link] is the subject of a more advanced course in quantum mechanics; here, we simply cite the results. The allowed energies are
The wave functions that correspond to these energies (the stationary states or states of definite energy) are
where , is the normalization constant, and is a polynomial of degree n called a Hermite polynomial . The first four Hermite polynomials are
A few sample wave functions are given in [link] . As the value of the principal number increases, the solutions alternate between even functions and odd functions about .
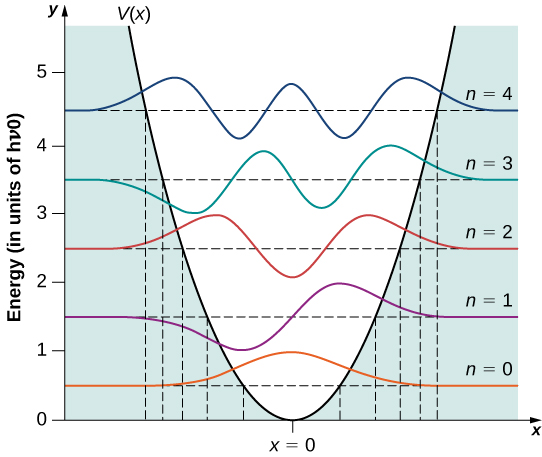
Several interesting features appear in this solution. Unlike a classical oscillator, the measured energies of a quantum oscillator can have only energy values given by [link] . Moreover, unlike the case for a quantum particle in a box, the allowable energy levels are evenly spaced,
When a particle bound to such a system makes a transition from a higher-energy state to a lower-energy state, the smallest-energy quantum carried by the emitted photon is necessarily hf . Similarly, when the particle makes a transition from a lower-energy state to a higher-energy state, the smallest-energy quantum that can be absorbed by the particle is hf . A quantum oscillator can absorb or emit energy only in multiples of this smallest-energy quantum. This is consistent with Planck’s hypothesis for the energy exchanges between radiation and the cavity walls in the blackbody radiation problem.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?