| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In ways reminiscent of thin-film interference, we consider two plane waves at X-ray wavelengths, each one reflecting off a different plane of atoms within a crystal’s lattice, as shown in [link] . From the geometry, the difference in path lengths is . Constructive interference results when this distance is an integer multiple of the wavelength. This condition is captured by the Bragg equation ,
where m is a positive integer and d is the spacing between the planes. Following the Law of Reflection, both the incident and reflected waves are described by the same angle, but unlike the general practice in geometric optics, is measured with respect to the surface itself, rather than the normal.
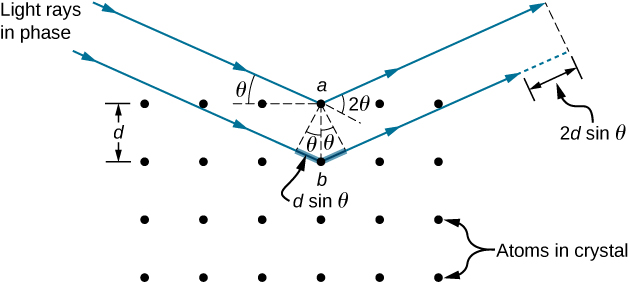
Check Your Understanding For the experiment described in [link] , what are the two other angles where interference maxima may be observed? What limits the number of maxima?
and ; Between , orders 1, 2, and 3, are all that exist.
Although [link] depicts a crystal as a two-dimensional array of scattering centers for simplicity, real crystals are structures in three dimensions. Scattering can occur simultaneously from different families of planes at different orientations and spacing patterns known as called Bragg planes , as shown in [link] . The resulting interference pattern can be quite complex.
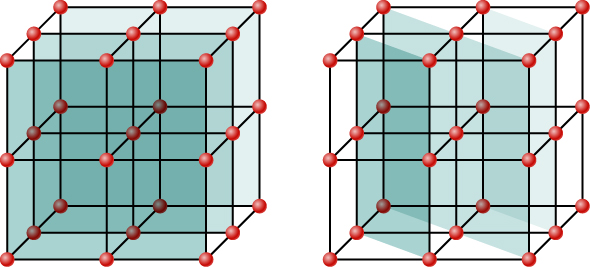
Crystal lattices can be examined with X-rays but not UV. Why?
UV wavelengths are much larger than lattice spacings in crystals such that there is no diffraction. The Bragg equation implies a value for sinθ greater than unity, which has no solution.
X-rays of wavelength 0.103 nm reflects off a crystal and a second-order maximum is recorded at a Bragg angle of . What is the spacing between the scattering planes in this crystal?
A first-order Bragg reflection maximum is observed when a monochromatic X-ray falls on a crystal at a angle to a reflecting plane. What is the wavelength of this X-ray?
0.120 nm
An X-ray scattering experiment is performed on a crystal whose atoms form planes separated by 0.440 nm. Using an X-ray source of wavelength 0.548 nm, what is the angle (with respect to the planes in question) at which the experimenter needs to illuminate the crystal in order to observe a first-order maximum?
The structure of the NaCl crystal forms reflecting planes 0.541 nm apart. What is the smallest angle, measured from these planes, at which X-ray diffraction can be observed, if X-rays of wavelength 0.085 nm are used?
On a certain crystal, a first-order X-ray diffraction maximum is observed at an angle of relative to its surface, using an X-ray source of unknown wavelength. Additionally, when illuminated with a different, this time of known wavelength 0.137 nm, a second-order maximum is detected at Determine (a) the spacing between the reflecting planes, and (b) the unknown wavelength.
Calcite crystals contain scattering planes separated by 0.30 nm. What is the angular separation between first and second-order diffraction maxima when X-rays of 0.130 nm wavelength are used?
The first-order Bragg angle for a certain crystal is . What is the second-order angle?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?