| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Electrical resistance can be considered as a measure of the frictional force in electrical current flow. Thus, electrical resistance is a primary source of energy dissipation in electrical systems such as electromagnets, electric motors, and transmission lines. Copper wire is commonly used in electrical wiring because it has one of the lowest room-temperature electrical resistivities among common conductors. (Actually, silver has a lower resistivity than copper, but the high cost and limited availability of silver outweigh its savings in energy over copper.)
Although our discussion of conductivity seems to imply that all materials must have electrical resistance, we know that this is not the case. When the temperature decreases below a critical value for many materials, their electrical resistivity drops to zero, and the materials become superconductors (see Superconductors ).
Watch this NOVA video excerpt, Making Stuff Colder, as an introduction to the topic of superconductivity and its many applications.
In addition to zero electrical resistance, superconductors also have perfect diamagnetism. In other words, in the presence of an applied magnetic field, the net magnetic field within a superconductor is always zero ( [link] ). Therefore, any magnetic field lines that pass through a superconducting sample when it is in its normal state are expelled once the sample becomes superconducting. These are manifestations of the Meissner effect, which you learned about in the chapter on current and resistance.
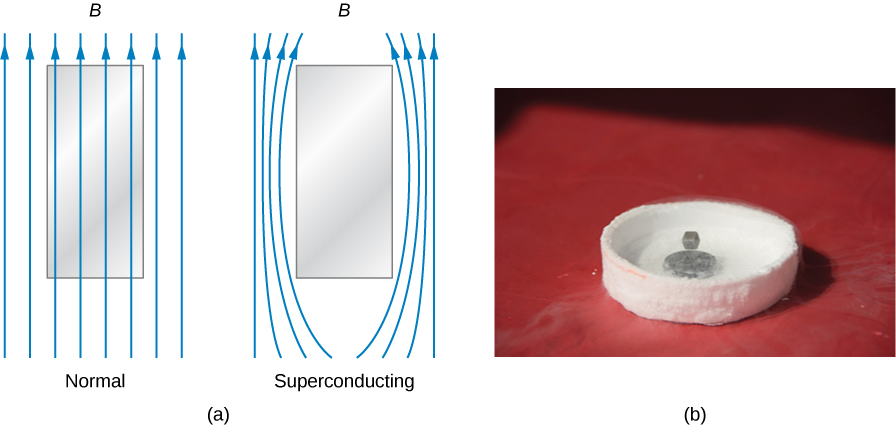
Interestingly, the Meissner effect is not a consequence of the resistance being zero. To see why, suppose that a sample placed in a magnetic field undergoes a transition in which its resistance drops to zero. From Ohm’s law, the current density, j , in the sample is related to the net internal electric field, E , and the resistivity by . If is zero, E must also be zero so that j can remain finite. Now E and the magnetic flux through the sample are related by Faraday’s law as
If E is zero, is also zero, that is, the magnetic flux through the sample cannot change. The magnetic field lines within the sample should therefore not be expelled when the transition occurs. Hence, it does not follow that a material whose resistance goes to zero has to exhibit the Meissner effect. Rather, the Meissner effect is a special property of superconductors.
Another important property of a superconducting material is its critical temperature , , the temperature below which the material is superconducting. The known range of critical temperatures is from a fraction of 1 K to slightly above 100 K. Superconductors with critical temperatures near this higher limit are commonly known as “high-temperature” superconductors. From a practical standpoint, superconductors for which are very important. At present, applications involving superconductors often still require that superconducting materials be immersed in liquid helium (4.2 K) in order to keep them below their critical temperature. The liquid helium baths must be continually replenished because of evaporation, and cooling costs can easily outweigh the savings in using a superconductor. However, 77 K is the temperature of liquid nitrogen, which is far more abundant and inexpensive than liquid helium. It would be much more cost-effective if we could easily fabricate and use high-temperature superconductor components that only need to be kept in liquid nitrogen baths to maintain their superconductivity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?