| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Physicists have long known that the strength of an interaction between particles depends on the distance of the interaction. For example, two positively charged particles experience a larger repulsive force at a short distance then at a long distance. In scattering experiments, the strength of an interaction depends on the energy of the interacting particle, since larger energy implies both closer and stronger interactions.
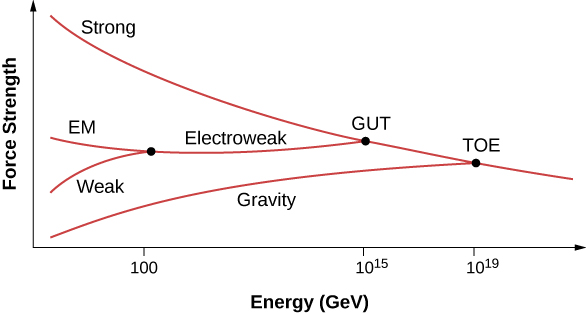
Particle physicists now suspect that the strength of all particle interactions (the four forces) merge at high energies, and the details of particle interactions at these energies can be described in terms of a single force ( [link] ). A unified theory describes what these interactions are like and explains why this description breaks down at low-energy scales. A grand unified theory is a theory that attempts to describe strong and electroweak interaction in terms of just one force. A theory of everything (TOE) takes the unification concept one step further. A TOE combines all four fundamental forces (including gravity) into one theory.
What is the Standard Model? Express your answer in terms of the four fundamental forces and exchange particles.
The Standard Model is a model of elementary particle interactions. This model contains the electroweak theory and quantum chromodynamics (QCD). It describes the interaction of leptons and quarks though the exchange of photons (electromagnetism) and bosons (weak theory), and the interaction of quark through the exchange of gluons (QCD). This model does not describe gravitational interactions.
Draw a Feynman diagram to represents annihilation of an electron and positron into a photon.
What is the motivation behind grand unification theories?
To explain particle interactions that involve the strong nuclear, electromagnetic, and weak nuclear forces in a unified way.
If a theory is developed that unifies all four forces, will it still be correct to say that the orbit of the Moon is determined by the gravitational force? Explain why.
If the Higgs boson is discovered and found to have mass, will it be considered the ultimate carrier of the weak force? Explain your response.
No, however it will explain why the W and Z bosons are massive (since the Higgs “imparts” mass to these particles), and therefore why the weak force is short ranged.
One of the common decay modes of the Even though only hadrons are involved in this decay, it occurs through the weak nuclear force. How do we know that this decay does not occur through the strong nuclear force?
Using the Heisenberg uncertainly principle, determine the range of the weak force if this force is produced by the exchange of a Z boson.
Use the Heisenberg uncertainly principle to estimate the range of a weak nuclear decay involving a graviton.
The graviton is massless, so like the photon is associated with a force of infinite range.
(a) The following decay is mediated by the electroweak force:
Draw the Feynman diagram for the decay.
(b) The following scattering is mediated by the electroweak force:
Draw the Feynman diagram for the scattering.
Assuming conservation of momentum, what is the energy of each ray produced in the decay of a neutral pion at rest, in the reaction ?
67.5 MeV
What is the wavelength of a 50-GeV electron, which is produced at SLAC? This provides an idea of the limit to the detail it can probe.
The primary decay mode for the negative pion is (a) What is the energy release in MeV in this decay? (b) Using conservation of momentum, how much energy does each of the decay products receive, given the is at rest when it decays? You may assume the muon antineutrino is massless and has momentum , just like a photon.
a. 33.9 MeV; b. By conservation of momentum, . By conservation of energy,
Suppose you are designing a proton decay experiment and you can detect 50 percent of the proton decays in a tank of water. (a) How many kilograms of water would you need to see one decay per month, assuming a lifetime of (b) How many cubic meters of water is this? (c) If the actual lifetime is , how long would you have to wait on an average to see a single proton decay?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?