| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To illustrate this interpretation, consider the simple case of a particle that can occupy a small container either at or ( [link] ). In classical physics, we assume the particle is located either at or when the observer is not looking. However, in quantum mechanics, the particle may exist in a state of indefinite position—that is, it may be located at and when the observer is not looking. The assumption that a particle can only have one value of position (when the observer is not looking) is abandoned. Similar comments can be made of other measurable quantities, such as momentum and energy.

The bizarre consequences of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics are illustrated by a creative thought experiment first articulated by Erwin Schrödinger ( National Geographic , 2013) ( [link] ):
“A cat is placed in a steel box along with a Geiger counter, a vial of poison, a hammer, and a radioactive substance. When the radioactive substance decays, the Geiger detects it and triggers the hammer to release the poison, which subsequently kills the cat. The radioactive decay is a random [probabilistic] process, and there is no way to predict when it will happen. Physicists say the atom exists in a state known as a superposition—both decayed and not decayed at the same time. Until the box is opened, an observer doesn’t know whether the cat is alive or dead—because the cat’s fate is intrinsically tied to whether or not the atom has decayed and the cat would [according to the Copenhagen interpretation]be “living and dead ... in equal parts” until it is observed.”
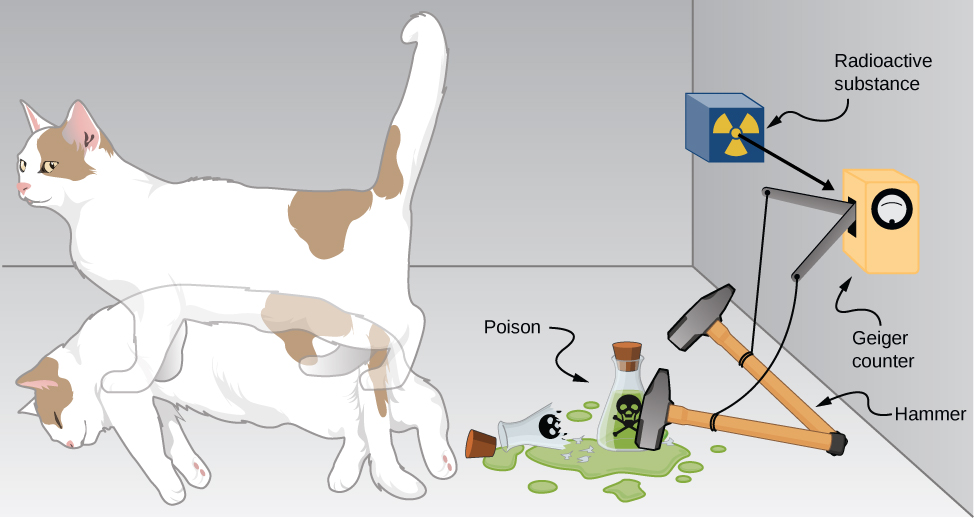
Schrödinger took the absurd implications of this thought experiment (a cat simultaneously dead and alive) as an argument against the Copenhagen interpretation. However, this interpretation remains the most commonly taught view of quantum mechanics.
Two-state systems (left and right, atom decays and does not decay, and so on) are often used to illustrate the principles of quantum mechanics. These systems find many applications in nature, including electron spin and mixed states of particles, atoms, and even molecules. Two-state systems are also finding application in the quantum computer, as mentioned in the introduction of this chapter. Unlike a digital computer, which encodes information in binary digits (zeroes and ones), a quantum computer stores and manipulates data in the form of quantum bits, or qubits. In general, a qubit is not in a state of zero or one, but rather in a mixed state of zero and one. If a large number of qubits are placed in the same quantum state, the measurement of an individual qubit would produce a zero with a probability p , and a one with a probability Many scientists believe that quantum computers are the future of the computer industry.
Later in this section, you will see how to use the wave function to describe particles that are “free” or bound by forces to other particles. The specific form of the wave function depends on the details of the physical system. A peculiarity of quantum theory is that these functions are usually complex function s . A complex function is one that contains one or more imaginary numbers . Experimental measurements produce real (nonimaginary) numbers only, so the above procedure to use the wave function must be slightly modified. In general, the probability that a particle is found in the narrow interval ( x , x + dx ) at time t is given by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?