| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When a metal surface is exposed to a monochromatic electromagnetic wave of sufficiently short wavelength (or equivalently, above a threshold frequency), the incident radiation is absorbed and the exposed surface emits electrons. This phenomenon is known as the photoelectric effect . Electrons that are emitted in this process are called photoelectrons .
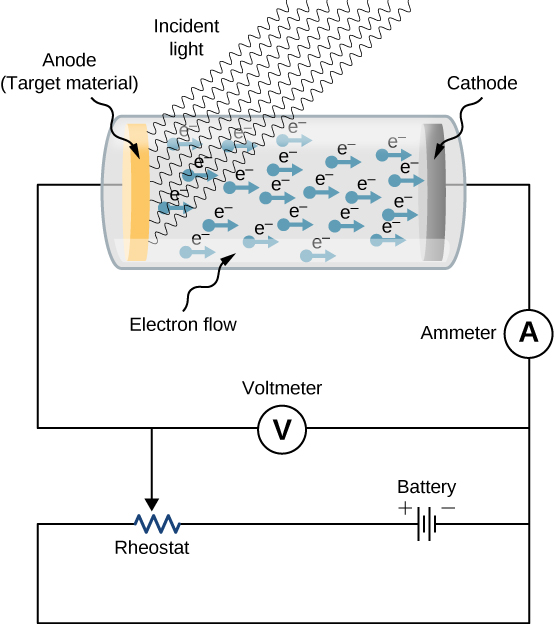
The experimental setup to study the photoelectric effect is shown schematically in [link] . The target material serves as the anode, which becomes the emitter of photoelectrons when it is illuminated by monochromatic radiation. We call this electrode the photoelectrode . Photoelectrons are collected at the cathode, which is kept at a lower potential with respect to the anode. The potential difference between the electrodes can be increased or decreased, or its polarity can be reversed. The electrodes are enclosed in an evacuated glass tube so that photoelectrons do not lose their kinetic energy on collisions with air molecules in the space between electrodes.
When the target material is not exposed to radiation, no current is registered in this circuit because the circuit is broken (note, there is a gap between the electrodes). But when the target material is connected to the negative terminal of a battery and exposed to radiation, a current is registered in this circuit; this current is called the photocurrent . Suppose that we now reverse the potential difference between the electrodes so that the target material now connects with the positive terminal of a battery, and then we slowly increase the voltage. The photocurrent gradually dies out and eventually stops flowing completely at some value of this reversed voltage. The potential difference at which the photocurrent stops flowing is called the stopping potential .
The photoelectric effect has three important characteristics that cannot be explained by classical physics: (1) the absence of a lag time, (2) the independence of the kinetic energy of photoelectrons on the intensity of incident radiation, and (3) the presence of a cut-off frequency. Let’s examine each of these characteristics.
When radiation strikes the target material in the electrode, electrons are emitted almost instantaneously, even at very low intensities of incident radiation. This absence of lag time contradicts our understanding based on classical physics. Classical physics predicts that for low-energy radiation, it would take significant time before irradiated electrons could gain sufficient energy to leave the electrode surface; however, such an energy buildup is not observed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?