| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Beginning in this section, we study crystalline solids, which consist of atoms arranged in an extended regular pattern called a lattice . Solids that do not or are unable to form crystals are classified as amorphous solids . Although amorphous solids (like glass) have a variety of interesting technological applications, the focus of this chapter will be on crystalline solids.
Atoms arrange themselves in a lattice to form a crystal because of a net attractive force between their constituent electrons and atomic nuclei. The crystals formed by the bonding of atoms belong to one of three categories, classified by their bonding: ionic, covalent, and metallic. Molecules can also bond together to form crystals; these bonds, not discussed here, are classified as molecular. Early in the twentieth century, the atomic model of a solid was speculative. We now have direct evidence of atoms in solids ( [link] ).
Many solids form by ionic bonding. A prototypical example is the sodium chloride crystal, as we discussed earlier. Electrons transfer from sodium atoms to adjacent chlorine atoms, since the valence electrons in sodium are loosely bound and chlorine has a large electron affinity. The positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chlorine (chloride) ions organize into an extended regular array of atoms ( [link] ).
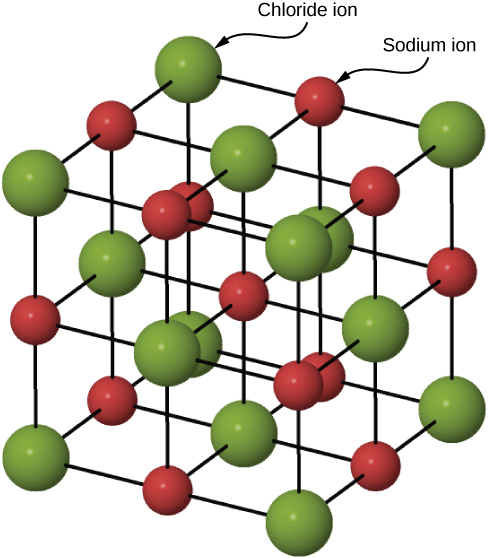
The charge distributions of the sodium and chloride ions are spherically symmetric, and the chloride ion is about two times the diameter of the sodium ion. The lowest energy arrangement of these ions is called the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. In this structure, each ion is closest to six ions of the other species. The unit cell is a cube—an atom occupies the center and corners of each “face” of the cube. The attractive potential energy of the ion due to the fields of these six ions is written
where the minus sign designates an attractive potential (and we identify ). At a distance are its next-nearest neighbors: twelve ions of the same charge. The total repulsive potential energy associated with these ions is
Next closest are eight ions a distance from the ion. The potential energy of the ion in the field of these eight ions is
Continuing in the same manner with alternate sets of and ions, we find that the net attractive potential energy of the single ion can be written as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?