| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we consider the effects of electron spin. Spin introduces two additional quantum numbers to our model of the hydrogen atom. Both were discovered by looking at the fine structure of atomic spectra. Spin is a fundamental characteristic of all particles, not just electrons, and is analogous to the intrinsic spin of extended bodies about their own axes, such as the daily rotation of Earth.
Spin is quantized in the same manner as orbital angular momentum. It has been found that the magnitude of the intrinsic spin angular momentum S of an electron is given by
where s is defined to be the spin quantum number . This is similar to the quantization of L given in [link] , except that the only value allowed for s for an electron is The electron is said to be a “spin-half particle.” The spin projection quantum number is associated with the z -components of spin, expressed by
In general, the allowed quantum numbers are
For the special case of an electron ( ),
Directions of intrinsic spin are quantized, just as they were for orbital angular momentum. The state is called the “spin-down” state and has a z -component of spin, ; state is called the “spin-up” state and has a z -component of spin, These states are shown in [link] .
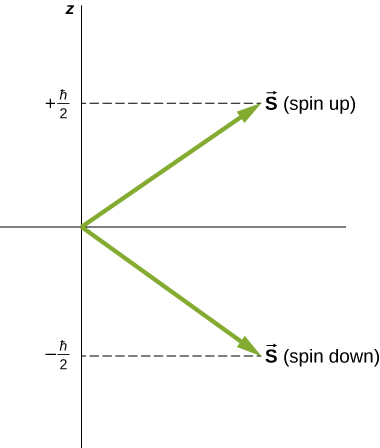
The intrinsic magnetic dipole moment of an electron can also be expressed in terms of the spin quantum number. In analogy to the orbital angular momentum, the magnitude of the electron magnetic moment is
According to the special theory of relativity, this value is low by a factor of 2. Thus, in vector form, the spin magnetic moment is
The z -component of the magnetic moment is
The spin projection quantum number has just two values so the z- component of the magnetic moment also has just two values:
where is one Bohr magneton. An electron is magnetic, so we expect the electron to interact with other magnetic fields. We consider two special cases: the interaction of a free electron with an external (nonuniform) magnetic field, and an electron in a hydrogen atom with a magnetic field produced by the orbital angular momentum of the electron.
The potential energy associated with the interaction between the electron magnetic moment and the external magnetic field is
The frequency of light emitted is proportional to the energy ( ) difference between these two states.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?