| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom in nature and, therefore, a good starting point to study atoms and atomic structure. The hydrogen atom consists of a single negatively charged electron that moves about a positively charged proton ( [link] ). In Bohr’s model, the electron is pulled around the proton in a perfectly circular orbit by an attractive Coulomb force. The proton is approximately 1800 times more massive than the electron, so the proton moves very little in response to the force on the proton by the electron. (This is analogous to the Earth-Sun system, where the Sun moves very little in response to the force exerted on it by Earth.) An explanation of this effect using Newton’s laws is given in Photons and Matter Waves .
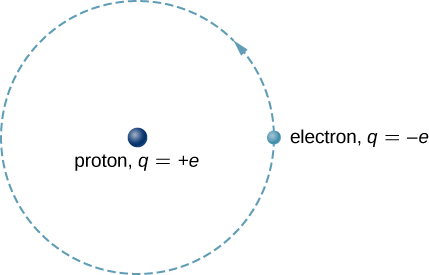
With the assumption of a fixed proton, we focus on the motion of the electron.
In the electric field of the proton, the potential energy of the electron is
where and r is the distance between the electron and the proton. As we saw earlier, the force on an object is equal to the negative of the gradient (or slope) of the potential energy function. For the special case of a hydrogen atom, the force between the electron and proton is an attractive Coulomb force.
Notice that the potential energy function U ( r ) does not vary in time. As a result, Schrödinger’s equation of the hydrogen atom reduces to two simpler equations: one that depends only on space ( x , y , z ) and another that depends only on time ( t ). (The separation of a wave function into space- and time-dependent parts for time-independent potential energy functions is discussed in Quantum Mechanics .) We are most interested in the space-dependent equation:
where is the three-dimensional wave function of the electron, is the mass of the electron, and E is the total energy of the electron. Recall that the total wave function is the product of the space-dependent wave function and the time-dependent wave function .
In addition to being time-independent, U ( r ) is also spherically symmetrical. This suggests that we may solve Schrödinger’s equation more easily if we express it in terms of the spherical coordinates instead of rectangular coordinates . A spherical coordinate system is shown in [link] . In spherical coordinates, the variable r is the radial coordinate, is the polar angle (relative to the vertical z -axis), and is the azimuthal angle (relative to the x -axis). The relationship between spherical and rectangular coordinates is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?