| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As discussed in the chapter on sound, if a source of sound and a listener are moving farther apart, the listener encounters fewer cycles of a wave in each second, and therefore lower frequency, than if their separation remains constant. For the same reason, the listener detects a higher frequency if the source and listener are getting closer. The resulting Doppler shift in detected frequency occurs for any form of wave. For sound waves, however, the equations for the Doppler shift differ markedly depending on whether it is the source, the observer, or the air, which is moving. Light requires no medium, and the Doppler shift for light traveling in vacuum depends only on the relative speed of the observer and source.
Suppose an observer in S sees light from a source in moving away at velocity v ( [link] ). The wavelength of the light could be measured within —for example, by using a mirror to set up standing waves and measuring the distance between nodes. These distances are proper lengths with as their rest frame, and change by a factor when measured in the observer’s frame S , where the ruler measuring the wavelength in is seen as moving.
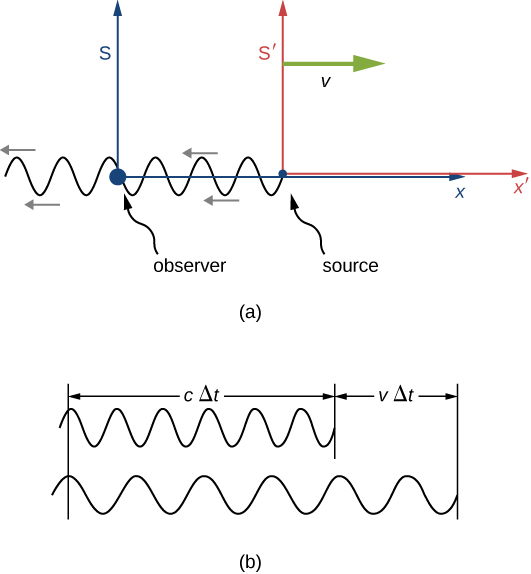
If the source were stationary in S , the observer would see a length of the wave pattern in time But because of the motion of relative to S , considered solely within S , the observer sees the wave pattern, and therefore the wavelength, stretched out by a factor of
as illustrated in (b) of [link] . The overall increase from both effects gives
where is the wavelength of the light seen by the source in and is the wavelength that the observer detects within S .
The observed wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is longer (called a “red shift”) than that emitted by the source when the source moves away from the observer. Similarly, the wavelength is shorter (called a “blue shift”) when the source moves toward the observer. The amount of change is determined by
where is the wavelength in the frame of reference of the source, and v is the relative velocity of the two frames S and The velocity v is positive for motion away from an observer and negative for motion toward an observer. In terms of source frequency and observed frequency, this equation can be written as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?