| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The length of the train car in [link] is the same for all the passengers. All of them would agree on the simultaneous location of the two ends of the car and obtain the same result for the distance between them. But simultaneous events in one inertial frame need not be simultaneous in another. If the train could travel at relativistic speeds, an observer on the ground would see the simultaneous locations of the two endpoints of the car at a different distance apart than observers inside the car. Measured distances need not be the same for different observers when relativistic speeds are involved.

Two observers passing each other always see the same value of their relative speed. Even though time dilation implies that the train passenger and the observer standing alongside the tracks measure different times for the train to pass, they still agree that relative speed, which is distance divided by elapsed time, is the same. If an observer on the ground and one on the train measure a different time for the length of the train to pass the ground observer, agreeing on their relative speed means they must also see different distances traveled.
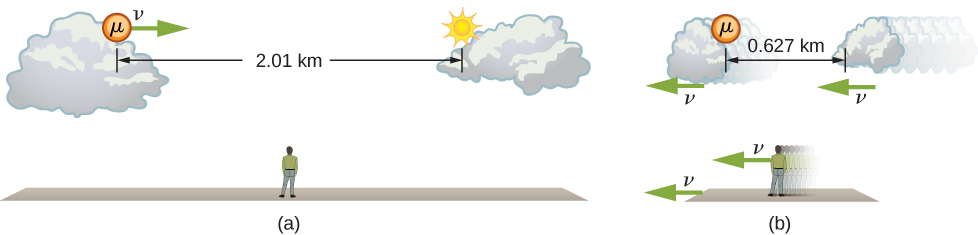
The muon discussed in [link] illustrates this concept ( [link] ). To an observer on Earth, the muon travels at 0.950 c for 7.05 μs from the time it is produced until it decays. Therefore, it travels a distance relative to Earth of:
In the muon frame, the lifetime of the muon is 2.20 μs. In this frame of reference, the Earth, air, and ground have only enough time to travel:
The distance between the same two events (production and decay of a muon) depends on who measures it and how they are moving relative to it.
Proper length is the distance between two points measured by an observer who is at rest relative to both of the points.
The earthbound observer measures the proper length because the points at which the muon is produced and decays are stationary relative to Earth. To the muon, Earth, air, and clouds are moving, so the distance L it sees is not the proper length.
To relate distances measured by different observers, note that the velocity relative to the earthbound observer in our muon example is given by
The time relative to the earthbound observer is because the object being timed is moving relative to this observer. The velocity relative to the moving observer is given by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?