| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When we studied interference in Young’s double-slit experiment, we ignored the diffraction effect in each slit. We assumed that the slits were so narrow that on the screen you saw only the interference of light from just two point sources. If the slit is smaller than the wavelength, then [link] (a) shows that there is just a spreading of light and no peaks or troughs on the screen. Therefore, it was reasonable to leave out the diffraction effect in that chapter. However, if you make the slit wider, [link] (b) and (c) show that you cannot ignore diffraction. In this section, we study the complications to the double-slit experiment that arise when you also need to take into account the diffraction effect of each slit.
To calculate the diffraction pattern for two (or any number of) slits, we need to generalize the method we just used for a single slit. That is, across each slit, we place a uniform distribution of point sources that radiate Huygens wavelets, and then we sum the wavelets from all the slits. This gives the intensity at any point on the screen. Although the details of that calculation can be complicated, the final result is quite simple:
The diffraction pattern of two slits of width D that are separated by a distance d is the interference pattern of two point sources separated by d multiplied by the diffraction pattern of a slit of width D .
In other words, the locations of the interference fringes are given by the equation , the same as when we considered the slits to be point sources, but the intensities of the fringes are now reduced by diffraction effects, according to [link] . [Note that in the chapter on interference, we wrote and used the integer m to refer to interference fringes. [link] also uses m , but this time to refer to diffraction minima. If both equations are used simultaneously, it is good practice to use a different variable (such as n ) for one of these integers in order to keep them distinct.]
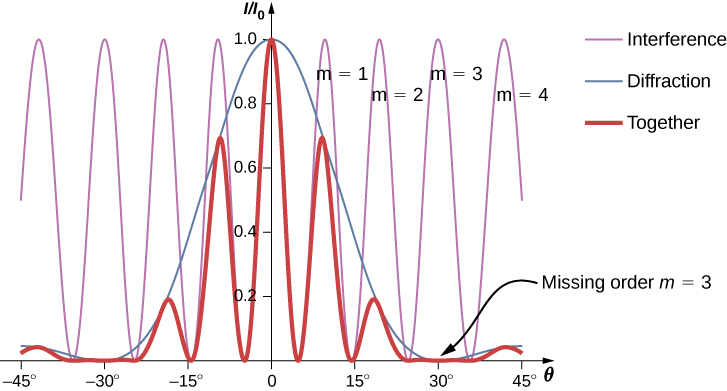
Interference and diffraction effects operate simultaneously and generally produce minima at different angles. This gives rise to a complicated pattern on the screen, in which some of the maxima of interference from the two slits are missing if the maximum of the interference is in the same direction as the minimum of the diffraction. We refer to such a missing peak as a missing order . One example of a diffraction pattern on the screen is shown in [link] . The solid line with multiple peaks of various heights is the intensity observed on the screen. It is a product of the interference pattern of waves from separate slits and the diffraction of waves from within one slit.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?