| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
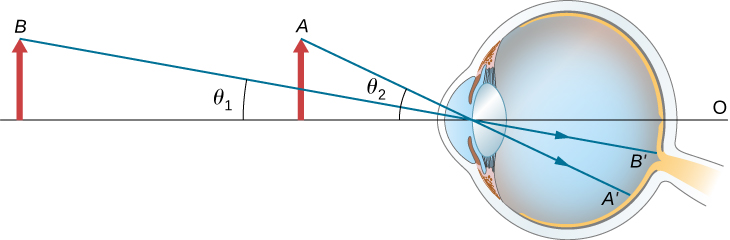
The apparent size of an object perceived by the eye depends on the angle the object subtends from the eye. As shown in [link] , the object at A subtends a larger angle from the eye than when it is position at point B . Thus, the object at A forms a larger image on the retina (see ) than when it is positioned at B (see ). Thus, objects that subtend large angles from the eye appear larger because they form larger images on the retina.
We have seen that, when an object is placed within a focal length of a convex lens, its image is virtual, upright, and larger than the object (see part (b) of [link] ). Thus, when such an image produced by a convex lens serves as the object for the eye, as shown in [link] , the image on the retina is enlarged, because the image produced by the lens subtends a larger angle in the eye than does the object. A convex lens used for this purpose is called a magnifying glass or a simple magnifier .

To account for the magnification of a magnifying lens, we compare the angle subtended by the image (created by the lens) with the angle subtended by the object (viewed with no lens), as shown in [link] . We assume that the object is situated at the near point of the eye, because this is the object distance at which the unaided eye can form the largest image on the retina. We will compare the magnified images created by a lens with this maximum image size for the unaided eye. The magnification of an image when observed by the eye is the angular magnification M , which is defined by the ratio of the angle subtended by the image to the angle subtended by the object:
Consider the situation shown in [link] . The magnifying lens is held a distance from the eye, and the image produced by the magnifier forms a distance L from the eye. We want to calculate the angular magnification for any arbitrary L and . In the small-angle approximation, the angular size of the image is . The angular size of the object at the near point is . The angular magnification is then
Using [link] for linear magnification
and the thin-lens equation
in [link] , we arrive at the following expression for the angular magnification of a magnifying lens:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?