| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The boundary between the microwave and infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is not well defined (see [link] ). Infrared radiation is generally produced by thermal motion, and the vibration and rotation of atoms and molecules. Electronic transitions in atoms and molecules can also produce infrared radiation . About half of the solar energy arriving at Earth is in the infrared region, with most of the rest in the visible part of the spectrum. About 23% of the solar energy is absorbed in the atmosphere, about 48% is absorbed at Earth’s surface, and about 29% is reflected back into space. http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/EnergyBalance/page4.php
The range of infrared frequencies extends up to the lower limit of visible light, just below red. In fact, infrared means “below red.” Water molecules rotate and vibrate particularly well at infrared frequencies. Reconnaissance satellites can detect buildings, vehicles, and even individual humans by their infrared emissions, whose power radiation is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature. More mundanely, we use infrared lamps, including those called quartz heaters , to preferentially warm us because we absorb infrared better than our surroundings.
The familiar handheld “remotes” for changing channels and settings on television sets often transmit their signal by modulating an infrared beam. If you try to use a TV remote without the infrared emitter being in direct line of sight with the infrared detector, you may find the television not responding. Some remotes use Bluetooth instead and reduce this annoyance.
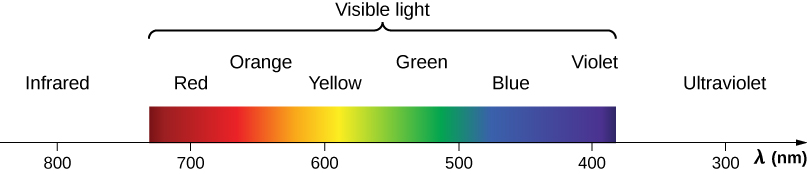
Visible light is the narrow segment of the electromagnetic spectrum between about 400 nm and about 750 nm to which the normal human eye responds. Visible light is produced by vibrations and rotations of atoms and molecules, as well as by electronic transitions within atoms and molecules. The receivers or detectors of light largely utilize electronic transitions.
Red light has the lowest frequencies and longest wavelengths, whereas violet has the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths ( [link] ). Blackbody radiation from the Sun peaks in the visible part of the spectrum but is more intense in the red than in the violet, making the sun yellowish in appearance.
Living things—plants and animals—have evolved to utilize and respond to parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in which they are embedded. We enjoy the beauty of nature through visible light. Plants are more selective. Photosynthesis uses parts of the visible spectrum to make sugars.
Ultraviolet means “above violet.” The electromagnetic frequencies of ultraviolet radiation (UV) extend upward from violet, the highest-frequency visible light. The highest-frequency ultraviolet overlaps with the lowest-frequency X-rays. The wavelengths of ultraviolet extend from 400 nm down to about 10 nm at its highest frequencies. Ultraviolet is produced by atomic and molecular motions and electronic transitions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?