| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
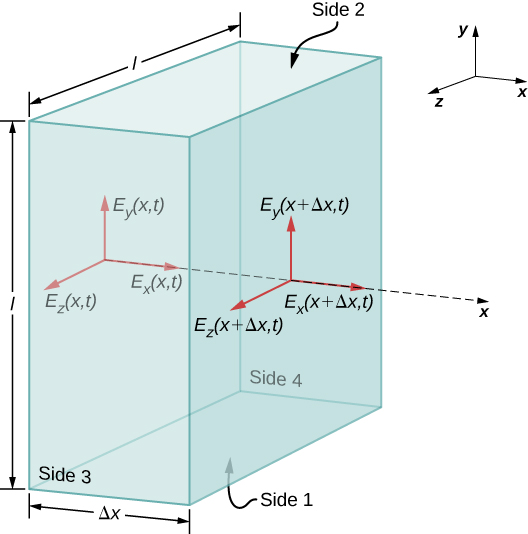
A similar argument holds by substituting E for B and using Gauss’s law for magnetism instead of Gauss’s law for electric fields. This shows that the B field is also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. The electromagnetic wave is therefore a transverse wave, with its oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to its direction of propagation.
We can next apply Maxwell’s equations to the description given in connection with [link] in the previous section to obtain an equation for the E field from the changing B field, and for the B field from a changing E field. We then combine the two equations to show how the changing E and B fields propagate through space at a speed precisely equal to the speed of light.
First, we apply Faraday’s law over Side 3 of the Gaussian surface, using the path shown in [link] . Because we have
Assuming is small and approximating by
we obtain
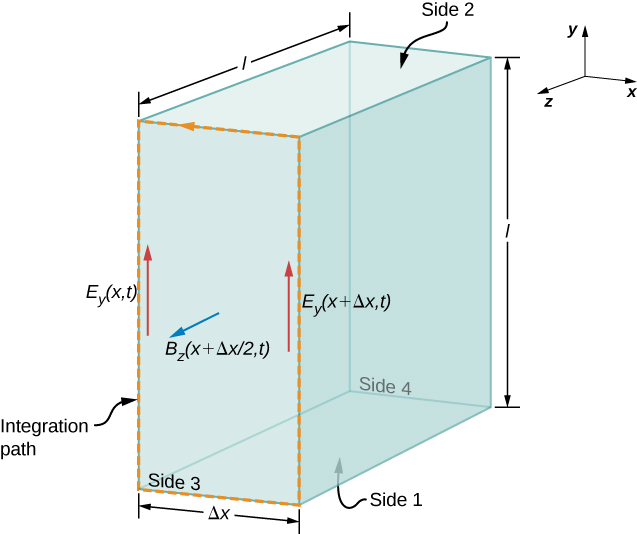
Because is small, the magnetic flux through the face can be approximated by its value in the center of the area traversed, namely . The flux of the B field through Face 3 is then the B field times the area,
From Faraday’s law,
Therefore, from [link] and [link] ,
Canceling and taking the limit as , we are left with
We could have applied Faraday’s law instead to the top surface (numbered 2) in [link] , to obtain the resulting equation
This is the equation describing the spatially dependent E field produced by the time-dependent B field.
Next we apply the Ampère-Maxwell law (with ) over the same two faces (Surface 3 and then Surface 2) of the rectangular box of [link] . Applying [link] ,
to Surface 3, and then to Surface 2, yields the two equations
These equations describe the spatially dependent B field produced by the time-dependent E field.
We next combine the equations showing the changing B field producing an E field with the equation showing the changing E field producing a B field. Taking the derivative of [link] with respect to x and using [link] gives
This is the form taken by the general wave equation for our plane wave. Because the equations describe a wave traveling at some as-yet-unspecified speed c , we can assume the field components are each functions of x – ct for the wave traveling in the + x -direction, that is,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?