| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Another popular type of capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor . It consists of an oxidized metal in a conducting paste. The main advantage of an electrolytic capacitor is its high capacitance relative to other common types of capacitors. For example, capacitance of one type of aluminum electrolytic capacitor can be as high as 1.0 F. However, you must be careful when using an electrolytic capacitor in a circuit, because it only functions correctly when the metal foil is at a higher potential than the conducting paste. When reverse polarization occurs, electrolytic action destroys the oxide film. This type of capacitor cannot be connected across an alternating current source, because half of the time, ac voltage would have the wrong polarity, as an alternating current reverses its polarity (see Alternating-Current Circuts on alternating-current circuits).
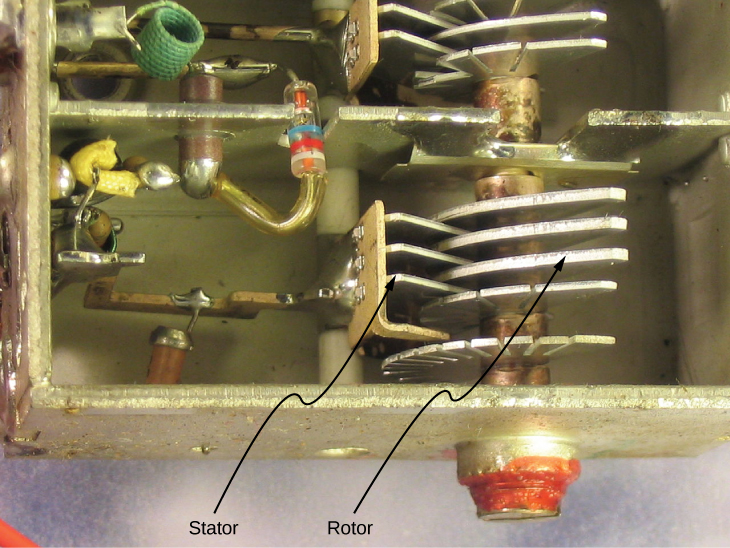
A variable air capacitor ( [link] ) has two sets of parallel plates. One set of plates is fixed (indicated as “stator”), and the other set of plates is attached to a shaft that can be rotated (indicated as “rotor”). By turning the shaft, the cross-sectional area in the overlap of the plates can be changed; therefore, the capacitance of this system can be tuned to a desired value. Capacitor tuning has applications in any type of radio transmission and in receiving radio signals from electronic devices. Any time you tune your car radio to your favorite station, think of capacitance.
The symbols shown in [link] are circuit representations of various types of capacitors. We generally use the symbol shown in [link] (a). The symbol in [link] (c) represents a variable-capacitance capacitor. Notice the similarity of these symbols to the symmetry of a parallel-plate capacitor. An electrolytic capacitor is represented by the symbol in part [link] (b), where the curved plate indicates the negative terminal.
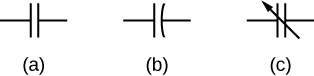
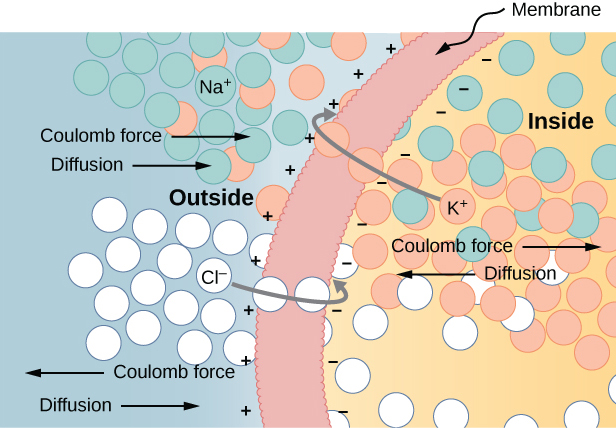
An interesting applied example of a capacitor model comes from cell biology and deals with the electrical potential in the plasma membrane of a living cell ( [link] ). Cell membranes separate cells from their surroundings but allow some selected ions to pass in or out of the cell. The potential difference across a membrane is about 70 mV. The cell membrane may be 7 to 10 nm thick. Treating the cell membrane as a nano-sized capacitor, the estimate of the smallest electrical field strength across its ‘plates’ yields the value .
This magnitude of electrical field is great enough to create an electrical spark in the air.
Visit the PhET Explorations: Capacitor Lab to explore how a capacitor works. Change the size of the plates and add a dielectric to see the effect on capacitance. Change the voltage and see charges built up on the plates. Observe the electrical field in the capacitor. Measure the voltage and the electrical field.
Does the capacitance of a device depend on the applied voltage? Does the capacitance of a device depend on the charge residing on it?
no; yes
Would you place the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor closer together or farther apart to increase their capacitance?
The value of the capacitance is zero if the plates are not charged. True or false?
false
If the plates of a capacitor have different areas, will they acquire the same charge when the capacitor is connected across a battery?
Does the capacitance of a spherical capacitor depend on which sphere is charged positively or negatively?
no
What charge is stored in a capacitor when 120.0 V is applied to it?
21.6 mC
Find the charge stored when 5.50 V is applied to an 8.00-pF capacitor.
Calculate the voltage applied to a capacitor when it holds of charge.
1.55 V
What voltage must be applied to an 8.00-nF capacitor to store 0.160 mC of charge?
What capacitance is needed to store of charge at a voltage of 120 V?
25.0 nF
What is the capacitance of a large Van de Graaff generator’s terminal, given that it stores 8.00 mC of charge at a voltage of 12.0 MV?
The plates of an empty parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 5.0 pF are 2.0 mm apart. What is the area of each plate?
A 60.0-pF vacuum capacitor has a plate area of . What is the separation between its plates?
A set of parallel plates has a capacitance of . How much charge must be added to the plates to increase the potential difference between them by 100 V?
500 µ C
Consider Earth to be a spherical conductor of radius 6400 km and calculate its capacitance.
If the capacitance per unit length of a cylindrical capacitor is 20 pF/m, what is the ratio of the radii of the two cylinders?
1:16
An empty parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance of . How much charge must leak off its plates before the voltage across them is reduced by 100 V?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?