| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
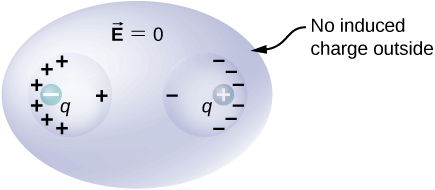
If a conductor has two cavities, one of them having a charge inside it and the other a charge the polarization of the conductor results in on the inside surface of the cavity a , on the inside surface of the cavity b , and on the outside surface ( [link] ). The charges on the surfaces may not be uniformly spread out; their spread depends upon the geometry. The only rule obeyed is that when the equilibrium has been reached, the charge distribution in a conductor is such that the electric field by the charge distribution in the conductor cancels the electric field of the external charges at all space points inside the body of the conductor.
| Definition of electric flux, for uniform electric field | |
| Electric flux through an open surface | |
| Electric flux through a closed surface | |
| Gauss’s law | |
| Gauss’s Law for systems with symmetry | |
| The magnitude of the electric field just outside the surface of a conductor |
Is the electric field inside a metal always zero?
Under electrostatic conditions, the excess charge on a conductor resides on its surface. Does this mean that all the conduction electrons in a conductor are on the surface?
yes
A charge q is placed in the cavity of a conductor as shown below. Will a charge outside the conductor experience an electric field due to the presence of q ?
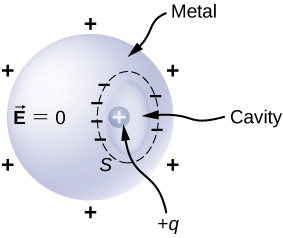
The conductor in the preceding figure has an excess charge of . If a point charge is placed in the cavity, what is the net charge on the surface of the cavity and on the outer surface of the conductor?
Since the electric field is zero inside a conductor, a charge of is induced on the inside surface of the cavity. This will put a charge of on the outside surface leaving a net charge of on the surface.
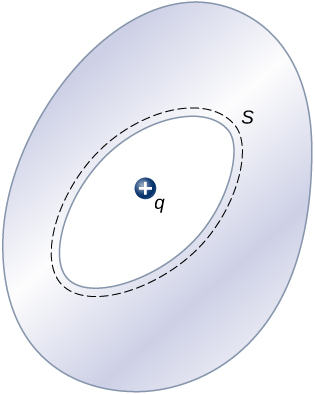
An uncharged conductor with an internal cavity is shown in the following figure. Use the closed surface S along with Gauss’ law to show that when a charge q is placed in the cavity a total charge – q is induced on the inner surface of the conductor. What is the charge on the outer surface of the conductor?
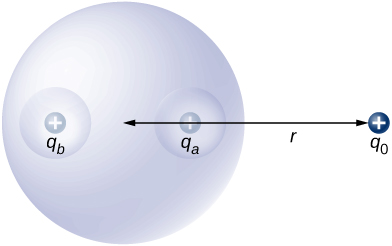
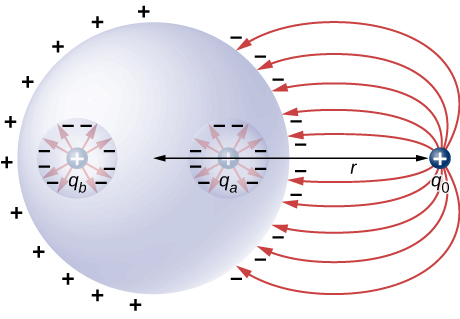
An uncharged spherical conductor S of radius R has two spherical cavities A and B of radii a and b , respectively as shown below. Two point charges and are placed at the center of the two cavities by using non-conducting supports. In addition, a point charge is placed outside at a distance r from the center of the sphere. (a) Draw approximate charge distributions in the metal although metal sphere has no net charge. (b) Draw electric field lines. Draw enough lines to represent all distinctly different places.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?