| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
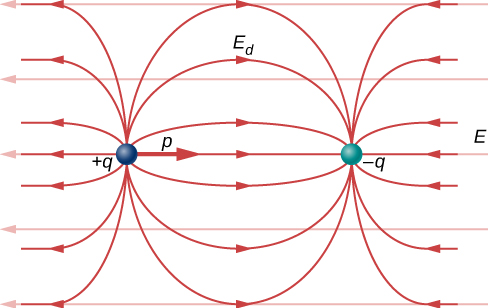
Recall that we found the electric field of a dipole in [link] . If we rewrite it in terms of the dipole moment we get:
The form of this field is shown in [link] . Notice that along the plane perpendicular to the axis of the dipole and midway between the charges, the direction of the electric field is opposite that of the dipole and gets weaker the further from the axis one goes. Similarly, on the axis of the dipole (but outside it), the field points in the same direction as the dipole, again getting weaker the further one gets from the charges.
| Coulomb’s law | |
| Superposition of electric forces | |
| Electric force due to an electric field | |
| Electric field at point P | |
| Field of an infinite wire | |
| Field of an infinite plane | |
| Dipole moment | |
| Torque on dipole in external E-field |
What are the stable orientation(s) for a dipole in an external electric field? What happens if the dipole is slightly perturbed from these orientations?
Consider the equal and opposite charges shown below. (a) Show that at all points on the x -axis for which (b) Show that at all points on the y -axis for which
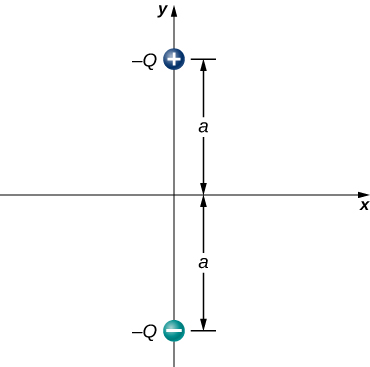
,
(a) What is the dipole moment of the configuration shown above? If , (b) what is the torque on this dipole with an electric field of ? (c) What is the torque on this dipole with an electric field of ? (d) What is the torque on this dipole with an electric field of ?
A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded with one oxygen atom. The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is (see below). Calculate the net dipole moment of a water molecule that is placed in a uniform, horizontal electric field of magnitude (You are missing some information for solving this problem; you will need to determine what information you need, and look it up.)
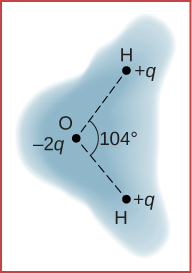
The net dipole moment of the molecule is the vector sum of the individual dipole moments between the two O-H. The separation O-H is 0.9578 angstroms:
Point charges and are located at and . What is the force of

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?