| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The velocity can be written as the angular velocity times the radius and the differential length written as dr . Therefore,
which is the same solution as before.
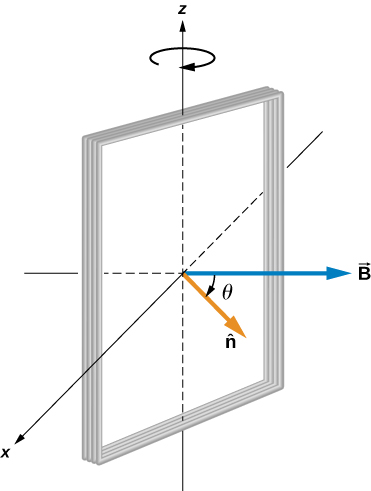
From Faraday’s law, the emf induced in the coil is
The constant angular velocity is The angle represents the time evolution of the angular velocity or . This is changes the function to time space rather than . The induced emf therefore varies sinusoidally with time according to
where
Check Your Understanding Shown below is a rod of length l that is rotated counterclockwise around the axis through O by the torque due to Assuming that the rod is in a uniform magnetic field , what is the emf induced between the ends of the rod when its angular velocity is ? Which end of the rod is at a higher potential?
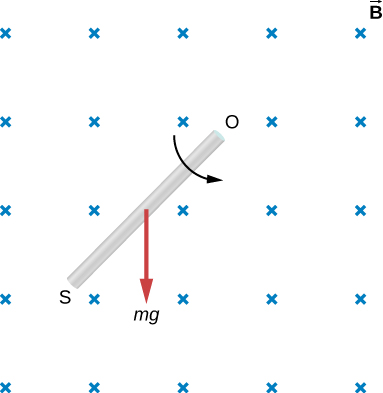
with O at a higher potential than S
Check Your Understanding A rod of length 10 cm moves at a speed of 10 m/s perpendicularly through a 1.5-T magnetic field. What is the potential difference between the ends of the rod?
1.5 V
A bar magnet falls under the influence of gravity along the axis of a long copper tube. If air resistance is negligible, will there be a force to oppose the descent of the magnet? If so, will the magnet reach a terminal velocity?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?