| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Touch the power supply of your laptop computer or some other device. It probably feels slightly warm. That heat is an unwanted byproduct of the process of converting household electric power into a current that can be used by your device. Although electric power is reasonably efficient, other losses are associated with it. As discussed in the section on power and energy, transmission of electric power produces line losses. These line losses exist whether the power is generated from conventional power plants (using coal, oil, or gas), nuclear plants, solar plants, hydroelectric plants, or wind farms. These losses can be reduced, but not eliminated, by transmitting using a higher voltage. It would be wonderful if these line losses could be eliminated, but that would require transmission lines that have zero resistance. In a world that has a global interest in not wasting energy, the reduction or elimination of this unwanted thermal energy would be a significant achievement. Is this possible?
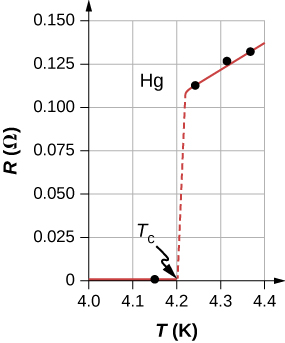
In 1911, Heike Kamerlingh Onnes of Leiden University, a Dutch physicist, was looking at the temperature dependence of the resistance of the element mercury. He cooled the sample of mercury and noticed the familiar behavior of a linear dependence of resistance on temperature; as the temperature decreased, the resistance decreased. Kamerlingh Onnes continued to cool the sample of mercury, using liquid helium. As the temperature approached , the resistance abruptly went to zero ( [link] ). This temperature is known as the critical temperature for mercury. The sample of mercury entered into a phase where the resistance was absolutely zero. This phenomenon is known as superconductivity . ( Note: If you connect the leads of a three-digit ohmmeter across a conductor, the reading commonly shows up as . The resistance of the conductor is not actually zero, it is less than .) There are various methods to measure very small resistances, such as the four-point method, but an ohmmeter is not an acceptable method to use for testing resistance in superconductivity.
As research continued, several other materials were found to enter a superconducting phase, when the temperature reached near absolute zero. In 1941, an alloy of niobium-nitride was found that could become superconducting at and in 1953, vanadium-silicon was found to become superconductive at The temperatures for the transition into superconductivity were slowly creeping higher. Strangely, many materials that make good conductors, such as copper, silver, and gold, do not exhibit superconductivity. Imagine the energy savings if transmission lines for electric power-generating stations could be made to be superconducting at temperatures near room temperature! A resistance of zero ohms means no losses and a great boost to reducing energy consumption. The problem is that is still very cold and in the range of liquid helium temperatures. At this temperature, it is not cost effective to transmit electrical energy because of the cooling requirements.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?