| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
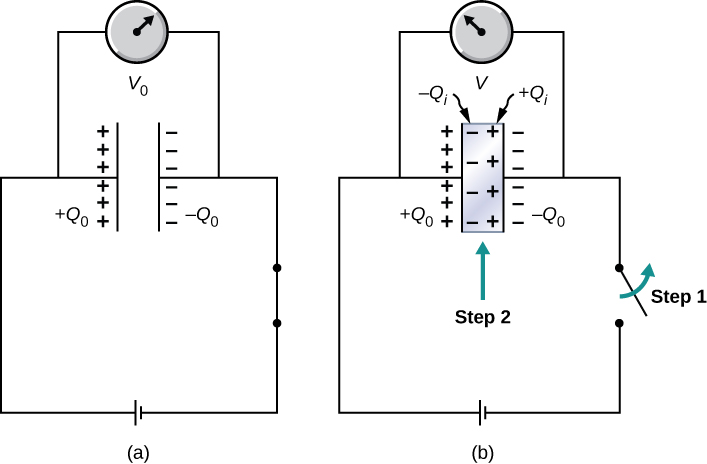
As we discussed earlier, an insulating material placed between the plates of a capacitor is called a dielectric. Inserting a dielectric between the plates of a capacitor affects its capacitance. To see why, let’s consider an experiment described in [link] . Initially, a capacitor with capacitance when there is air between its plates is charged by a battery to voltage . When the capacitor is fully charged, the battery is disconnected. A charge then resides on the plates, and the potential difference between the plates is measured to be . Now, suppose we insert a dielectric that totally fills the gap between the plates. If we monitor the voltage, we find that the voltmeter reading has dropped to a smaller value V . We write this new voltage value as a fraction of the original voltage , with a positive number , :
The constant in this equation is called the dielectric constant of the material between the plates, and its value is characteristic for the material. A detailed explanation for why the dielectric reduces the voltage is given in the next section. Different materials have different dielectric constants (a table of values for typical materials is provided in the next section). Once the battery becomes disconnected, there is no path for a charge to flow to the battery from the capacitor plates. Hence, the insertion of the dielectric has no effect on the charge on the plate, which remains at a value of . Therefore, we find that the capacitance of the capacitor with a dielectric is
This equation tells us that the capacitance of an empty (vacuum) capacitor can be increased by a factor of when we insert a dielectric material to completely fill the space between its plates . Note that [link] can also be used for an empty capacitor by setting . In other words, we can say that the dielectric constant of the vacuum is 1, which is a reference value.
The principle expressed by [link] is widely used in the construction industry ( [link] ). Metal plates in an electronic stud finder act effectively as a capacitor. You place a stud finder with its flat side on the wall and move it continually in the horizontal direction. When the finder moves over a wooden stud, the capacitance of its plates changes, because wood has a different dielectric constant than a gypsum wall. This change triggers a signal in a circuit, and thus the stud is detected.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?