| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The concept of flux describes how much of something goes through a given area. More formally, it is the dot product of a vector field (in this chapter, the electric field) with an area. You may conceptualize the flux of an electric field as a measure of the number of electric field lines passing through an area ( [link] ). The larger the area, the more field lines go through it and, hence, the greater the flux; similarly, the stronger the electric field is (represented by a greater density of lines), the greater the flux. On the other hand, if the area rotated so that the plane is aligned with the field lines, none will pass through and there will be no flux.
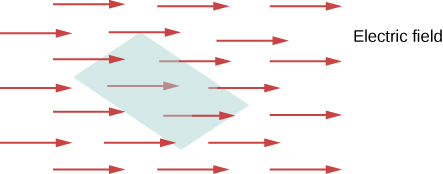
A macroscopic analogy that might help you imagine this is to put a hula hoop in a flowing river. As you change the angle of the hoop relative to the direction of the current, more or less of the flow will go through the hoop. Similarly, the amount of flow through the hoop depends on the strength of the current and the size of the hoop. Again, flux is a general concept; we can also use it to describe the amount of sunlight hitting a solar panel or the amount of energy a telescope receives from a distant star, for example.
To quantify this idea, [link] (a) shows a planar surface of area that is perpendicular to the uniform electric field If N field lines pass through , then we know from the definition of electric field lines ( Electric Charges and Fields ) that or
The quantity is the electric flux through . We represent the electric flux through an open surface like by the symbol . Electric flux is a scalar quantity and has an SI unit of newton-meters squared per coulomb ( ). Notice that may also be written as , demonstrating that electric flux is a measure of the number of field lines crossing a surface .

Now consider a planar surface that is not perpendicular to the field. How would we represent the electric flux? [link] (b) shows a surface of area that is inclined at an angle to the xz -plane and whose projection in that plane is (area ). The areas are related by Because the same number of field lines crosses both and , the fluxes through both surfaces must be the same. The flux through is therefore Designating as a unit vector normal to (see [link] (b)), we obtain

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?