| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Earlier in this chapter, we introduced the Clausius statement of the second law of thermodynamics, which is based on the irreversibility of spontaneous heat flow. As we remarked then, the second law of thermodynamics can be stated in several different ways, and all of them can be shown to imply the others. In terms of heat engines, the second law of thermodynamics may be stated as follows:
It is impossible to convert the heat from a single source into work without any other effect.
This is known as the Kelvin statement of the second law of thermodynamics . This statement describes an unattainable “ perfect engine ,” as represented schematically in [link] (a). Note that “without any other effect” is a very strong restriction. For example, an engine can absorb heat and turn it all into work, but not if it completes a cycle . Without completing a cycle, the substance in the engine is not in its original state and therefore an “other effect” has occurred. Another example is a chamber of gas that can absorb heat from a heat reservoir and do work isothermally against a piston as it expands. However, if the gas were returned to its initial state (that is, made to complete a cycle), it would have to be compressed and heat would have to be extracted from it.
The Kelvin statement is a manifestation of a well-known engineering problem. Despite advancing technology, we are not able to build a heat engine that is efficient. The first law does not exclude the possibility of constructing a perfect engine, but the second law forbids it.
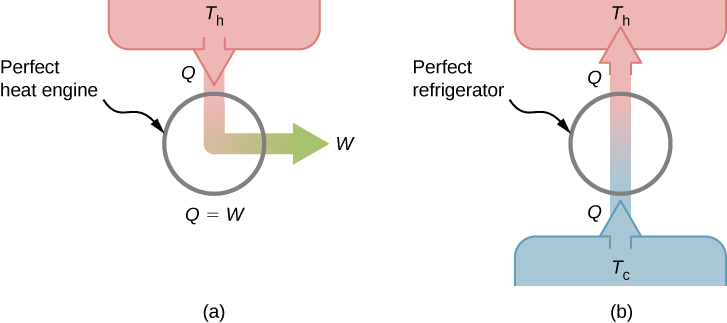
We can show that the Kelvin statement is equivalent to the Clausius statement if we view the two objects in the Clausius statement as a cold reservoir and a hot reservoir. Thus, the Clausius statement becomes: It is impossible to construct a refrigerator that transfers heat from a cold reservoir to a hot reservoir without aid from an external source . The Clausius statement is related to the everyday observation that heat never flows spontaneously from a cold object to a hot object. Heat transfer in the direction of increasing temperature always requires some energy input . A “ perfect refrigerator ,” shown in [link] (b), which works without such external aid, is impossible to construct.
To prove the equivalence of the Kelvin and Clausius statements, we show that if one statement is false, it necessarily follows that the other statement is also false. Let us first assume that the Clausius statement is false, so that the perfect refrigerator of [link] (b) does exist. The refrigerator removes heat Q from a cold reservoir at a temperature and transfers all of it to a hot reservoir at a temperature Now consider a real heat engine working in the same temperature range. It extracts heat from the hot reservoir, does work W , and discards heat Q to the cold reservoir. From the first law, these quantities are related by .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?