| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A variety of important phenomena and devices can be understood with Faraday’s law. In this section, we examine two of these.
Electric generators induce an emf by rotating a coil in a magnetic field, as briefly discussed in Motional Emf . We now explore generators in more detail. Consider the following example.
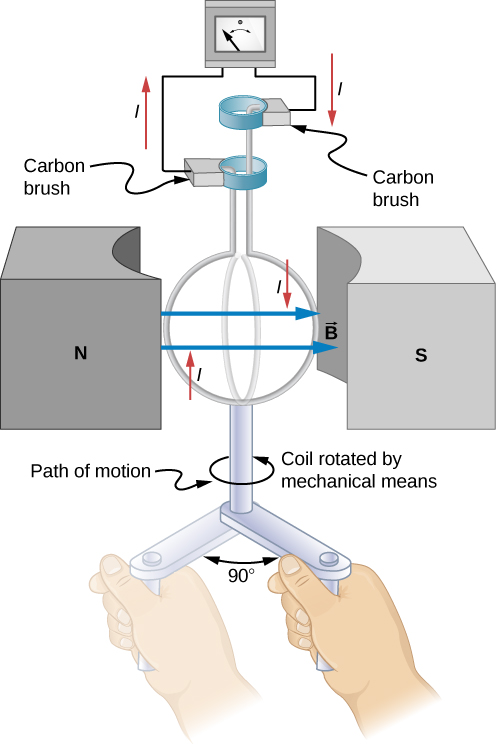
We recognize this situation as the same one in [link] . According to the diagram, the projection of the surface normal vector to the magnetic field is initially and this is inserted by the definition of the dot product. The magnitude of the magnetic field and area of the loop are fixed over time, which makes the integration simplify quickly. The induced emf is written out using Faraday’s law:
Entering this value gives
The emf calculated in [link] is the average over one-fourth of a revolution. What is the emf at any given instant? It varies with the angle between the magnetic field and a perpendicular to the coil. We can get an expression for emf as a function of time by considering the motional emf on a rotating rectangular coil of width w and height l in a uniform magnetic field, as illustrated in [link] .
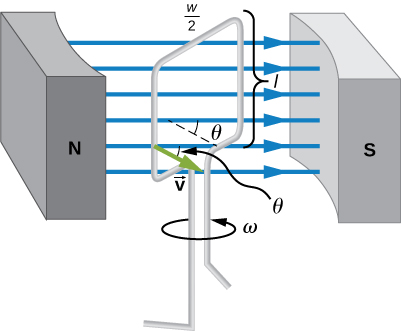
Charges in the wires of the loop experience the magnetic force, because they are moving in a magnetic field. Charges in the vertical wires experience forces parallel to the wire, causing currents. But those in the top and bottom segments feel a force perpendicular to the wire, which does not cause a current. We can thus find the induced emf by considering only the side wires. Motional emf is given to be , where the velocity v is perpendicular to the magnetic field B . Here the velocity is at an angle with B , so that its component perpendicular to B is v sin (see [link] ). Thus, in this case, the emf induced on each side is , and they are in the same direction. The total emf around the loop is then

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?