| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
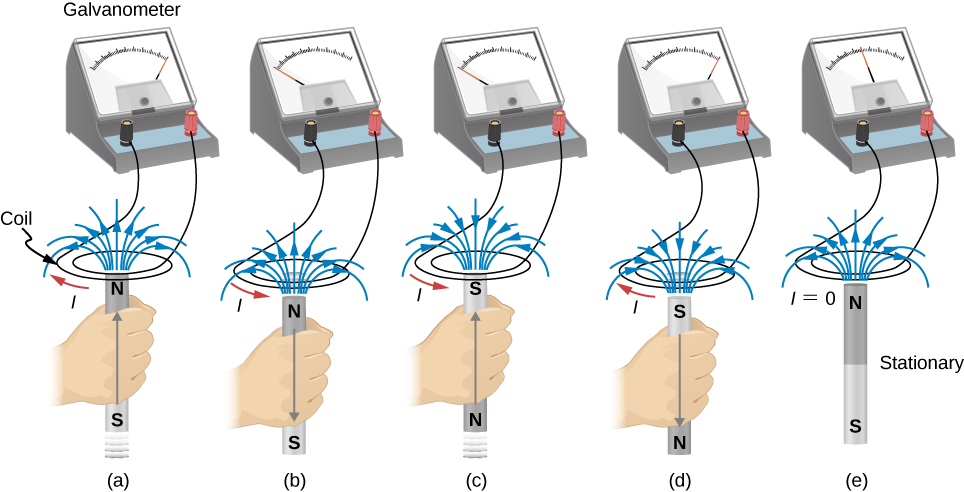
The first productive experiments concerning the effects of time-varying magnetic fields were performed by Michael Faraday in 1831. One of his early experiments is represented in [link] . An emf is induced when the magnetic field in the coil is changed by pushing a bar magnet into or out of the coil. Emfs of opposite signs are produced by motion in opposite directions, and the directions of emfs are also reversed by reversing poles. The same results are produced if the coil is moved rather than the magnet—it is the relative motion that is important. The faster the motion, the greater the emf, and there is no emf when the magnet is stationary relative to the coil.
Faraday also discovered that a similar effect can be produced using two circuits—a changing current in one circuit induces a current in a second, nearby circuit. For example, when the switch is closed in circuit 1 of [link] (a), the ammeter needle of circuit 2 momentarily deflects, indicating that a short-lived current surge has been induced in that circuit. The ammeter needle quickly returns to its original position, where it remains. However, if the switch of circuit 1 is now suddenly opened, another short-lived current surge in the direction opposite from before is observed in circuit 2.
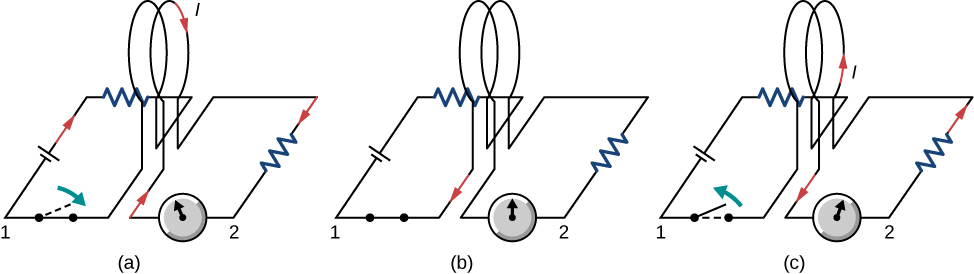
Faraday realized that in both experiments, a current flowed in the circuit containing the ammeter only when the magnetic field in the region occupied by that circuit was changing . As the magnet of the figure was moved, the strength of its magnetic field at the loop changed; and when the current in circuit 1 was turned on or off, the strength of its magnetic field at circuit 2 changed. Faraday was eventually able to interpret these and all other experiments involving magnetic fields that vary with time in terms of the following law:
The emf induced is the negative change in the magnetic flux per unit time. Any change in the magnetic field or change in orientation of the area of the coil with respect to the magnetic field induces a voltage (emf).
The magnetic flux is a measurement of the amount of magnetic field lines through a given surface area, as seen in [link] . This definition is similar to the electric flux studied earlier. This means that if we have

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?