| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You might expect that two current-carrying wires generate significant forces between them, since ordinary currents produce magnetic fields and these fields exert significant forces on ordinary currents. But you might not expect that the force between wires is used to define the ampere. It might also surprise you to learn that this force has something to do with why large circuit breakers burn up when they attempt to interrupt large currents.
The force between two long, straight, and parallel conductors separated by a distance r can be found by applying what we have developed in the preceding sections. [link] shows the wires, their currents, the field created by one wire, and the consequent force the other wire experiences from the created field. Let us consider the field produced by wire 1 and the force it exerts on wire 2 (call the force ). The field due to at a distance r is
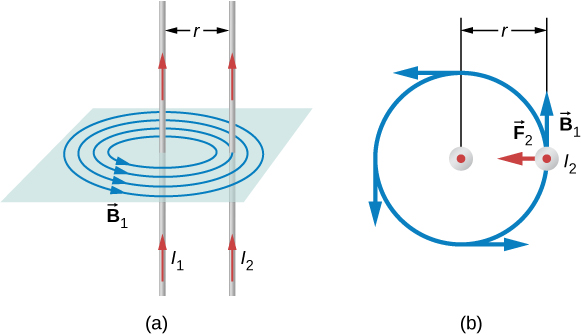
This field is uniform from the wire 1 and perpendicular to it, so the force it exerts on a length l of wire 2 is given by with
The forces on the wires are equal in magnitude, so we just write F for the magnitude of (Note that ) Since the wires are very long, it is convenient to think in terms of F/l , the force per unit length. Substituting the expression for into [link] and rearranging terms gives
The ratio F/l is the force per unit length between two parallel currents and separated by a distance r . The force is attractive if the currents are in the same direction and repulsive if they are in opposite directions.
This force is responsible for the pinch effect in electric arcs and other plasmas. The force exists whether the currents are in wires or not. It is only apparent if the overall charge density is zero; otherwise, the Coulomb repulsion overwhelms the magnetic attraction. In an electric arc, where charges are moving parallel to one another, an attractive force squeezes currents into a smaller tube. In large circuit breakers, such as those used in neighborhood power distribution systems, the pinch effect can concentrate an arc between plates of a switch trying to break a large current, burn holes, and even ignite the equipment. Another example of the pinch effect is found in the solar plasma, where jets of ionized material, such as solar flares, are shaped by magnetic forces.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?