| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have seen that mass produces a gravitational field and also interacts with that field. Charge produces an electric field and also interacts with that field. Since moving charge (that is, current) interacts with a magnetic field, we might expect that it also creates that field—and it does.
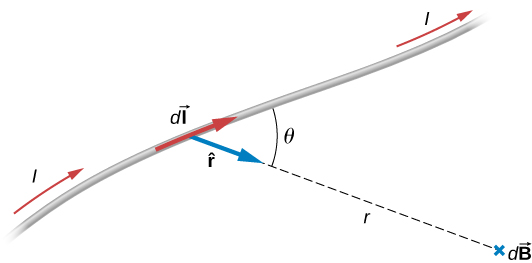
The equation used to calculate the magnetic field produced by a current is known as the Biot-Savart law. It is an empirical law named in honor of two scientists who investigated the interaction between a straight, current-carrying wire and a permanent magnet. This law enables us to calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by a current in a wire. The Biot-Savart law states that at any point P ( [link] ), the magnetic field due to an element of a current-carrying wire is given by
The constant is known as the permeability of free space and is exactly
in the SI system. The infinitesimal wire segment is in the same direction as the current I (assumed positive), r is the distance from to P and is a unit vector that points from to P , as shown in the figure.
The direction of is determined by applying the right-hand rule to the vector product The magnitude of is
where is the angle between and Notice that if then The field produced by a current element has no component parallel to
The magnetic field due to a finite length of current-carrying wire is found by integrating [link] along the wire, giving us the usual form of the Biot-Savart law.
The magnetic field due to an element of a current-carrying wire is given by
Since this is a vector integral, contributions from different current elements may not point in the same direction. Consequently, the integral is often difficult to evaluate, even for fairly simple geometries. The following strategy may be helpful.
To solve Biot-Savart law problems, the following steps are helpful:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?