| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Moving charges experience a force in a magnetic field. If these moving charges are in a wire—that is, if the wire is carrying a current—the wire should also experience a force. However, before we discuss the force exerted on a current by a magnetic field, we first examine the magnetic field generated by an electric current. We are studying two separate effects here that interact closely: A current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field and the magnetic field exerts a force on the current-carrying wire.
When discussing historical discoveries in magnetism, we mentioned Oersted’s finding that a wire carrying an electrical current caused a nearby compass to deflect. A connection was established that electrical currents produce magnetic fields. (This connection between electricity and magnetism is discussed in more detail in Sources of Magnetic Fields .)
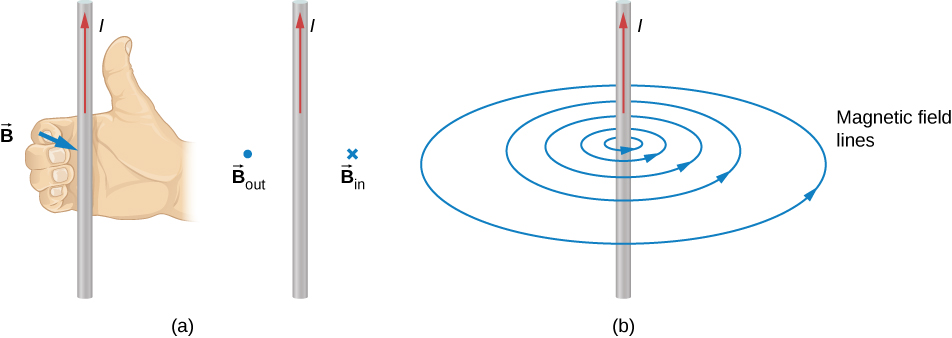
The compass needle near the wire experiences a force that aligns the needle tangent to a circle around the wire. Therefore, a current-carrying wire produces circular loops of magnetic field. To determine the direction of the magnetic field generated from a wire, we use a second right-hand rule. In RHR-2, your thumb points in the direction of the current while your fingers wrap around the wire, pointing in the direction of the magnetic field produced ( [link] ). If the magnetic field were coming at you or out of the page, we represent this with a dot. If the magnetic field were going into the page, we represent this with an These symbols come from considering a vector arrow: An arrow pointed toward you, from your perspective, would look like a dot or the tip of an arrow. An arrow pointed away from you, from your perspective, would look like a cross or an A composite sketch of the magnetic circles is shown in [link] , where the field strength is shown to decrease as you get farther from the wire by loops that are farther separated.
Electric current is an ordered movement of charge. A current-carrying wire in a magnetic field must therefore experience a force due to the field. To investigate this force, let’s consider the infinitesimal section of wire as shown in [link] . The length and cross-sectional area of the section are dl and A , respectively, so its volume is The wire is formed from material that contains n charge carriers per unit volume, so the number of charge carriers in the section is If the charge carriers move with drift velocity the current I in the wire is (from Current and Resistance )

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?