| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A charged particle experiences a force when moving through a magnetic field. What happens if this field is uniform over the motion of the charged particle? What path does the particle follow? In this section, we discuss the circular motion of the charged particle as well as other motion that results from a charged particle entering a magnetic field.
The simplest case occurs when a charged particle moves perpendicular to a uniform B -field ( [link] ). If the field is in a vacuum, the magnetic field is the dominant factor determining the motion. Since the magnetic force is perpendicular to the direction of travel, a charged particle follows a curved path in a magnetic field. The particle continues to follow this curved path until it forms a complete circle. Another way to look at this is that the magnetic force is always perpendicular to velocity, so that it does no work on the charged particle. The particle’s kinetic energy and speed thus remain constant. The direction of motion is affected but not the speed.
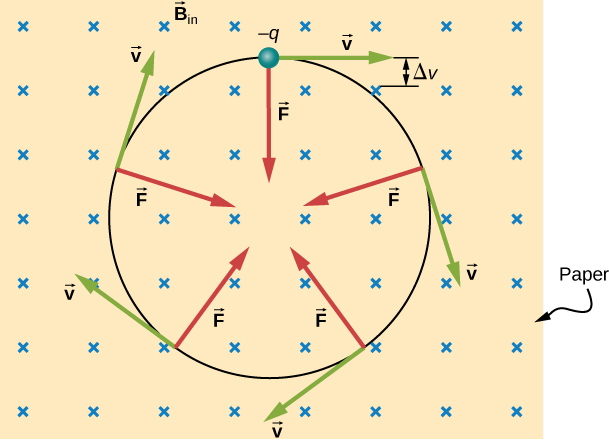
In this situation, the magnetic force supplies the centripetal force Noting that the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the magnitude of the magnetic force is reduced to Because the magnetic force F supplies the centripetal force we have
Solving for r yields
Here, r is the radius of curvature of the path of a charged particle with mass m and charge q , moving at a speed v that is perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength B . The time for the charged particle to go around the circular path is defined as the period, which is the same as the distance traveled (the circumference) divided by the speed. Based on this and [link] , we can derive the period of motion as
If the velocity is not perpendicular to the magnetic field, then we can compare each component of the velocity separately with the magnetic field. The component of the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field produces a magnetic force perpendicular to both this velocity and the field:
where is the angle between v and B . The component parallel to the magnetic field creates constant motion along the same direction as the magnetic field, also shown in [link] . The parallel motion determines the pitch p of the helix, which is the distance between adjacent turns. This distance equals the parallel component of the velocity times the period:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?