| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have outlined the properties of magnets, described how they behave, and listed some of the applications of magnetic properties. Even though there are no such things as isolated magnetic charges, we can still define the attraction and repulsion of magnets as based on a field. In this section, we define the magnetic field, determine its direction based on the right-hand rule, and discuss how to draw magnetic field lines.
A magnetic field is defined by the force that a charged particle experiences moving in this field, after we account for the gravitational and any additional electric forces possible on the charge. The magnitude of this force is proportional to the amount of charge q , the speed of the charged particle v , and the magnitude of the applied magnetic field. The direction of this force is perpendicular to both the direction of the moving charged particle and the direction of the applied magnetic field. Based on these observations, we define the magnetic field strength B based on the magnetic force on a charge q moving at velocity as the cross product of the velocity and magnetic field, that is,
In fact, this is how we define the magnetic field —in terms of the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field. The magnitude of the force is determined from the definition of the cross product as it relates to the magnitudes of each of the vectors. In other words, the magnitude of the force satisfies
where θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field.
The SI unit for magnetic field strength B is called the tesla (T) after the eccentric but brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla (1856–1943), where
A smaller unit, called the gauss (G), where is sometimes used. The strongest permanent magnets have fields near 2 T; superconducting electromagnets may attain 10 T or more. Earth’s magnetic field on its surface is only about or 0.5 G.
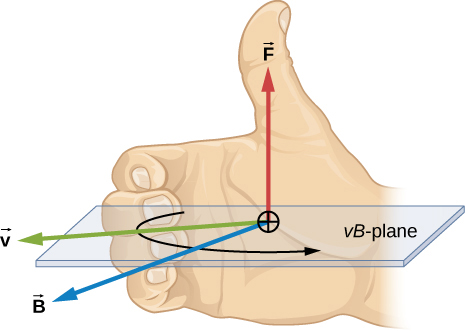
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane formed by and as determined by the right-hand rule-1 (or RHR-1), which is illustrated in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?