| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

There are a number of ways to represent organic compounds. It is useful to know all of these so that you can recognise a molecule however it is shown. There are three main ways of representing a compound. We will use the example of a molecule called 2-methylpropane to help explain the difference between each.
The molecular formula of a compound shows how many atoms of each type are in a molecule. The number of each atom is written as a subscript after the atomic symbol. The molecular formula of 2-methylpropane is:
C H
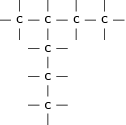
The structural formula of an organic compound shows every bond between every atom in the molecule. Each bond is represented by a line. The structural formula of 2-methylpropane is shown in [link] .

When a compound is represented using its condensed structural formula, each carbon atom and the hydrogen atoms that are bonded directly to it are listed as a molecular formula, followed by a similar molecular formula for the neighbouring carbon atom. Branched groups are shown in brackets after the carbon atom to which they are bonded. The condensed structural formula below shows that in 2-methylpropane, there is a branched chain attached to the second carbon atom of the main chain. You can check this by looking at the structural formula in [link] .
CH CH(CH )CH


It is possible for two organic compounds to have the same molecular formula but a different structural formula . Look for example at the two organic compounds that are shown in [link] .

If you were to count the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each compound, you would find that they are the same. They both have the same molecular formula (C H ), but their structure is different and so are their properties. Such compounds are called isomers .
In chemistry, isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula and often with the same kinds of chemical bonds between atoms, but in which the atoms are arranged differently.
Match the organic compound in Column A with its isomer Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| CH CH(CH )OH | CH CH(CH )CH |
 |
 |
 |
C H OH |
All organic compounds have a particular bond or group of atoms which we call its functional group . This group is important in determining how a compound will react.
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a specific group of atoms within molecules, that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction(s) regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of.
In one group of organic compounds called the hydrocarbons , the single, double and triple bonds of the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes are examples of functional groups. In another group, the alcohols, an oxygen and a hydrogen atom are bonded to each other to form the functional group for those compounds (in other words an alcohol has an OH in it). All alcohols will contain an oxygen and a hydrogen atom bonded together in some part of the molecule.
[link] summarises some of the common functional groups. We will look at these in more detail later in this chapter.
| Name of group | Functional group | Example | Diagram |
| Alk ane |
|
Ethane |
 |
| Alk ene |
|
Ethene |
 |
| Alk yne |
|
Ethyne (acetylene) |
|
| Halo-alkane |
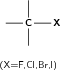 |
Chloroethane |
 |
| Alcoh ol / alkan ol |
|
Ethanol |
 |
| Carboxylic acid |
|
ethanoic acid |
|
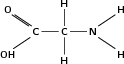
| Amine |
 |
Glycine |
 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?