| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding Find the angle between forces and in [link] .
Check Your Understanding How much work is done by the first dog and by the second dog in [link] on the displacement in [link] ?
,
Vector multiplication of two vectors yields a vector product.
The vector product of two vectors and is denoted by and is often referred to as a cross product . The vector product is a vector that has its direction perpendicular to both vectors and . In other words, vector is perpendicular to the plane that contains vectors and , as shown in [link] . The magnitude of the vector product is defined as
where angle , between the two vectors, is measured from vector (first vector in the product) to vector (second vector in the product), as indicated in [link] , and is between and .
According to [link] , the vector product vanishes for pairs of vectors that are either parallel or antiparallel because .
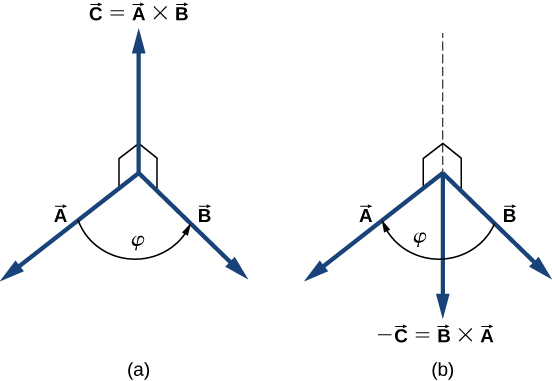
On the line perpendicular to the plane that contains vectors and there are two alternative directions—either up or down, as shown in [link] —and the direction of the vector product may be either one of them. In the standard right-handed orientation, where the angle between vectors is measured counterclockwise from the first vector, vector points upward , as seen in [link] (a). If we reverse the order of multiplication, so that now comes first in the product, then vector must point downward , as seen in [link] (b). This means that vectors and are antiparallel to each other and that vector multiplication is not commutative but anticommutative . The anticommutative property means the vector product reverses the sign when the order of multiplication is reversed:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?