| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
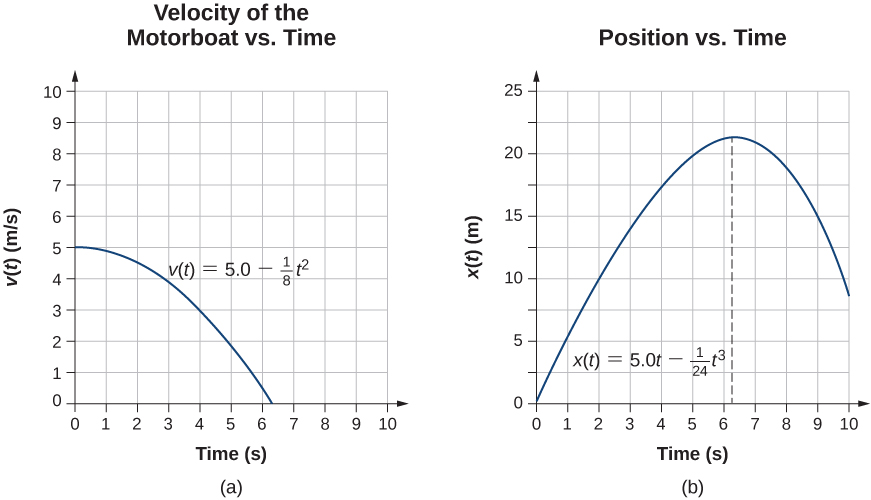
Check Your Understanding A particle starts from rest and has an acceleration function . (a) What is the velocity function? (b) What is the position function? (c) When is the velocity zero?
| Displacement | |
| Total displacement | |
| Average velocity | |
| Instantaneous velocity | |
| Average speed | |
| Instantaneous speed | |
| Average acceleration | |
| Instantaneous acceleration | |
| Position from average velocity | |
| Average velocity | |
| Velocity from acceleration | |
| Position from velocity and acceleration | |
| Velocity from distance | |
| Velocity of free fall | |
| Height of free fall | |
| Velocity of free fall from height | |
| Velocity from acceleration | |
| Position from velocity |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?