| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding If the normal force acting on each face of a cubical piece of steel is changed by find the resulting change in the volume of the piece of steel.
63 mL
The concepts of shear stress and strain concern only solid objects or materials. Buildings and tectonic plates are examples of objects that may be subjected to shear stresses. In general, these concepts do not apply to fluids.
Shear deformation occurs when two antiparallel forces of equal magnitude are applied tangentially to opposite surfaces of a solid object, causing no deformation in the transverse direction to the line of force, as in the typical example of shear stress illustrated in [link] . Shear deformation is characterized by a gradual shift of layers in the direction tangent to the acting forces. This gradation in occurs in the transverse direction along some distance Shear strain is defined by the ratio of the largest displacement to the transverse distance
Shear strain is caused by shear stress. Shear stress is due to forces that act parallel to the surface. We use the symbol for such forces. The magnitude per surface area A where shearing force is applied is the measure of shear stress
The shear modulus is the proportionality constant in [link] and is defined by the ratio of stress to strain. Shear modulus is commonly denoted by S :
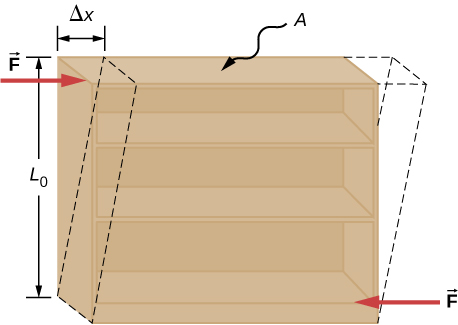
We can also find shear stress and strain, respectively:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?