| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A piece of putty and a tennis ball with the same mass are thrown against a wall with the same velocity. Which object experience a greater impulse from the wall or are the impulses equal? Explain.
A 75.0-kg person is riding in a car moving at 20.0 m/s when the car runs into a bridge abutment (see the following figure).
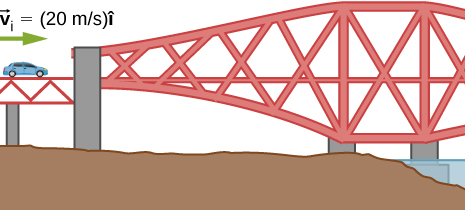
a. ; b.
One hazard of space travel is debris left by previous missions. There are several thousand objects orbiting Earth that are large enough to be detected by radar, but there are far greater numbers of very small objects, such as flakes of paint. Calculate the force exerted by a 0.100-mg chip of paint that strikes a spacecraft window at a relative speed of , given the collision lasts .
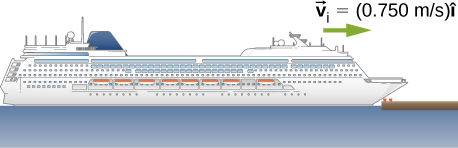
A cruise ship with a mass of strikes a pier at a speed of 0.750 m/s. It comes to rest after traveling 6.00 m, damaging the ship, the pier, and the tugboat captain’s finances. Calculate the average force exerted on the pier using the concept of impulse. ( Hint : First calculate the time it took to bring the ship to rest, assuming a constant force.)
Calculate the final speed of a 110-kg rugby player who is initially running at 8.00 m/s but collides head-on with a padded goalpost and experiences a backward force of for .
Water from a fire hose is directed horizontally against a wall at a rate of 50.0 kg/s and a speed of 42.0 m/s. Calculate the force exerted on the wall, assuming the water’s horizontal momentum is reduced to zero.
A 0.450-kg hammer is moving horizontally at 7.00 m/s when it strikes a nail and comes to rest after driving the nail 1.00 cm into a board. Assume constant acceleration of the hammer-nail pair.
What is the momentum (as a function of time) of a 5.0-kg particle moving with a velocity ? What is the net force acting on this particle?
;
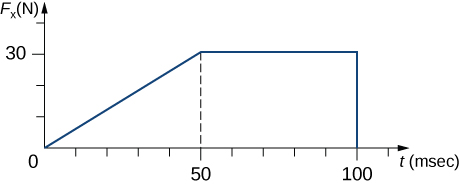
The x -component of a force on a 46-g golf ball by a 7-iron versus time is plotted in the following figure:
A hockey puck of mass 150 g is sliding due east on a frictionless table with a speed of 10 m/s. Suddenly, a constant force of magnitude 5 N and direction due north is applied to the puck for 1.5 s. Find the north and east components of the momentum at the end of the 1.5-s interval.
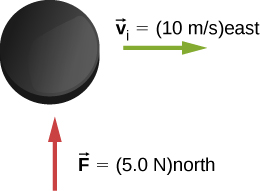
Let the positive x -axis be in the direction of the original momentum. Then and
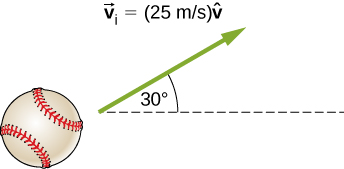
A ball of mass 250 g is thrown with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of with the horizontal direction. Ignore air resistance. What is the momentum of the ball after 0.2 s? (Do this problem by finding the components of the momentum first, and then constructing the magnitude and direction of the momentum vector from the components.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?