| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A physics major is cooking breakfast when she notices that the frictional force between her steel spatula and Teflon frying pan is only 0.200 N. Knowing the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two materials, she quickly calculates the normal force. What is it?
5.00 N
(a) When rebuilding his car’s engine, a physics major must exert N of force to insert a dry steel piston into a steel cylinder. What is the normal force between the piston and cylinder? (b) What force would he have to exert if the steel parts were oiled?
(a) What is the maximum frictional force in the knee joint of a person who supports 66.0 kg of her mass on that knee? (b) During strenuous exercise, it is possible to exert forces to the joints that are easily 10 times greater than the weight being supported. What is the maximum force of friction under such conditions? The frictional forces in joints are relatively small in all circumstances except when the joints deteriorate, such as from injury or arthritis. Increased frictional forces can cause further damage and pain.
a. 10.0 N; b. 97.0 N
Suppose you have a 120-kg wooden crate resting on a wood floor, with coefficient of static friction 0.500 between these wood surfaces. (a) What maximum force can you exert horizontally on the crate without moving it? (b) If you continue to exert this force once the crate starts to slip, what will its acceleration then be? The coefficient of sliding friction is known to be 0.300 for this situation.
(a) If half of the weight of a small utility truck is supported by its two drive wheels, what is the maximum acceleration it can achieve on dry concrete? (b) Will a metal cabinet lying on the wooden bed of the truck slip if it accelerates at this rate? (c) Solve both problems assuming the truck has four-wheel drive.
a. ; b. The cabinet will not slip. c. The cabinet will slip.
A team of eight dogs pulls a sled with waxed wood runners on wet snow (mush!). The dogs have average masses of 19.0 kg, and the loaded sled with its rider has a mass of 210 kg. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the dogs starting from rest if each dog exerts an average force of 185 N backward on the snow. (b) Calculate the force in the coupling between the dogs and the sled.
Consider the 65.0-kg ice skater being pushed by two others shown below. (a) Find the direction and magnitude of the total force exerted on her by the others, given that the magnitudes and are 26.4 N and 18.6 N, respectively. (b) What is her initial acceleration if she is initially stationary and wearing steel-bladed skates that point in the direction of (c) What is her acceleration assuming she is already moving in the direction of (Remember that friction always acts in the direction opposite that of motion or attempted motion between surfaces in contact.)
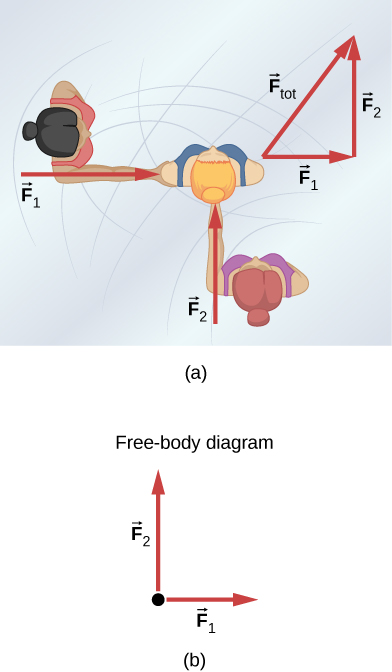
a. 32.3 N, b. 0; c. in the direction of
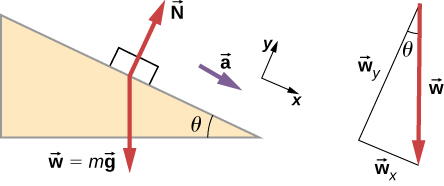
Show that the acceleration of any object down a frictionless incline that makes an angle with the horizontal is . (Note that this acceleration is independent of mass.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?