| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Success in problem solving is necessary to understand and apply physical principles. We developed a pattern of analyzing and setting up the solutions to problems involving Newton’s laws in Newton’s Laws of Motion ; in this chapter, we continue to discuss these strategies and apply a step-by-step process.
We follow here the basics of problem solving presented earlier in this text, but we emphasize specific strategies that are useful in applying Newton’s laws of motion . Once you identify the physical principles involved in the problem and determine that they include Newton’s laws of motion, you can apply these steps to find a solution. These techniques also reinforce concepts that are useful in many other areas of physics. Many problem-solving strategies are stated outright in the worked examples, so the following techniques should reinforce skills you have already begun to develop.
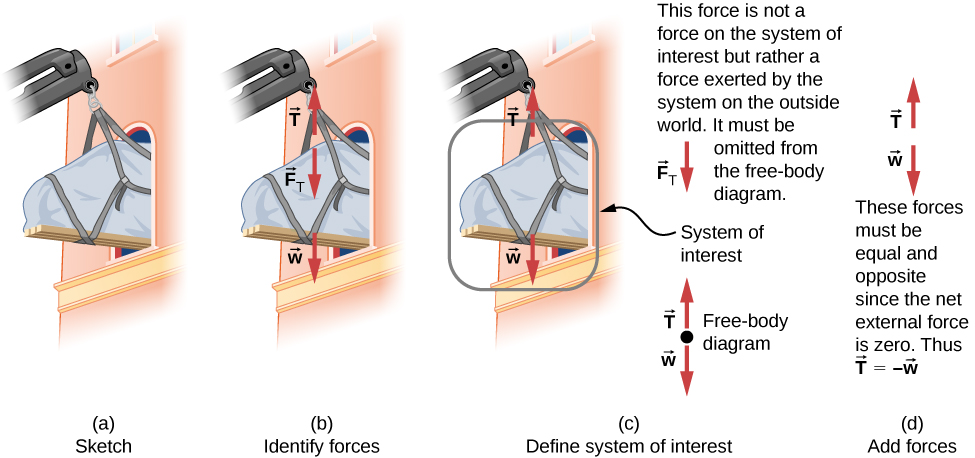
Let’s apply this problem-solving strategy to the challenge of lifting a grand piano into a second-story apartment. Once we have determined that Newton’s laws of motion are involved (if the problem involves forces), it is particularly important to draw a careful sketch of the situation. Such a sketch is shown in [link] (a). Then, as in [link] (b), we can represent all forces with arrows. Whenever sufficient information exists, it is best to label these arrows carefully and make the length and direction of each correspond to the represented force.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?