| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We studied gravitational potential energy in Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy , where the value of g remained constant. We now develop an expression that works over distances such that g is not constant. This is necessary to correctly calculate the energy needed to place satellites in orbit or to send them on missions in space.
We defined work and potential energy in Work and Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy . The usefulness of those definitions is the ease with which we can solve many problems using conservation of energy. Potential energy is particularly useful for forces that change with position, as the gravitational force does over large distances. In Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy , we showed that the change in gravitational potential energy near Earth’s surface is . This works very well if g does not change significantly between and . We return to the definition of work and potential energy to derive an expression that is correct over larger distances.
Recall that work ( W ) is the integral of the dot product between force and distance. Essentially, it is the product of the component of a force along a displacement times that displacement. We define as the negative of the work done by the force we associate with the potential energy. For clarity, we derive an expression for moving a mass m from distance from the center of Earth to distance . However, the result can easily be generalized to any two objects changing their separation from one value to another.
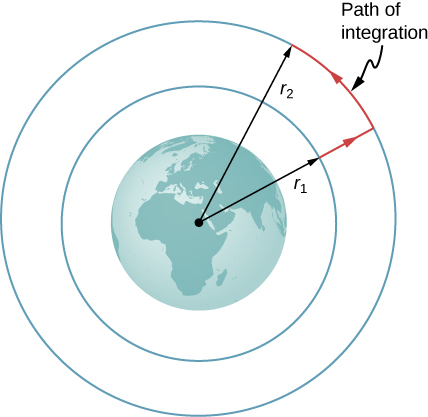
Consider [link] , in which we take m from a distance from Earth’s center to a distance that is from the center. Gravity is a conservative force (its magnitude and direction are functions of location only), so we can take any path we wish, and the result for the calculation of work is the same. We take the path shown, as it greatly simplifies the integration. We first move radially outward from distance to distance , and then move along the arc of a circle until we reach the final position. During the radial portion, is opposite to the direction we travel along , so Along the arc, is perpendicular to , so . No work is done as we move along the arc. Using the expression for the gravitational force and noting the values for along the two segments of our path, we have
Since , we can adopt a simple expression for :
Note two important items with this definition. First, . The potential energy is zero when the two masses are infinitely far apart. Only the difference in U is important, so the choice of is merely one of convenience. (Recall that in earlier gravity problems, you were free to take at the top or bottom of a building, or anywhere.) Second, note that U becomes increasingly more negative as the masses get closer. That is consistent with what you learned about potential energy in Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy . As the two masses are separated, positive work must be done against the force of gravity, and hence, U increases (becomes less negative). All masses naturally fall together under the influence of gravity, falling from a higher to a lower potential energy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?