| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
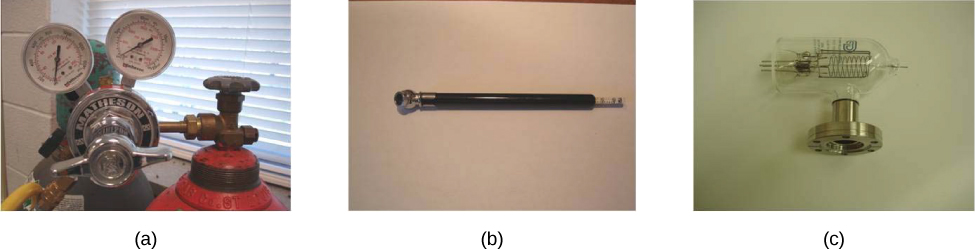
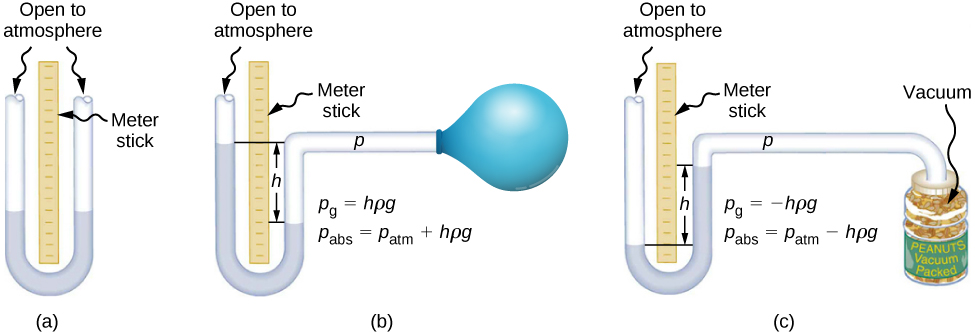
One of the most important classes of pressure gauges applies the property that pressure due to the weight of a fluid of constant density is given by . The U-shaped tube shown in [link] is an example of a manometer ; in part (a), both sides of the tube are open to the atmosphere, allowing atmospheric pressure to push down on each side equally so that its effects cancel.
A manometer with only one side open to the atmosphere is an ideal device for measuring gauge pressures. The gauge pressure is and is found by measuring h . For example, suppose one side of the U-tube is connected to some source of pressure such as the balloon in part (b) of the figure or the vacuum-packed peanut jar shown in part (c). Pressure is transmitted undiminished to the manometer, and the fluid levels are no longer equal. In part (b), is greater than atmospheric pressure, whereas in part (c), is less than atmospheric pressure. In both cases, differs from atmospheric pressure by an amount where is the density of the fluid in the manometer. In part (b), can support a column of fluid of height h , so it must exert a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure (the gauge pressure is positive). In part (c), atmospheric pressure can support a column of fluid of height h , so is less than atmospheric pressure by an amount (the gauge pressure is negative).
Manometers typically use a U-shaped tube of a fluid (often mercury) to measure pressure. A barometer (see [link] ) is a device that typically uses a single column of mercury to measure atmospheric pressure. The barometer, invented by the Italian mathematician and physicist Evangelista Torricelli (1608–1647) in 1643, is constructed from a glass tube closed at one end and filled with mercury. The tube is then inverted and placed in a pool of mercury. This device measures atmospheric pressure, rather than gauge pressure, because there is a nearly pure vacuum above the mercury in the tube. The height of the mercury is such that . When atmospheric pressure varies, the mercury rises or falls.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?