| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Suppose a fluid is moving but its depth is constant—that is, . Under this condition, Bernoulli’s equation becomes
Situations in which fluid flows at a constant depth are so common that this equation is often also called Bernoulli’s principle , which is simply Bernoulli’s equation for fluids at constant depth. (Note again that this applies to a small volume of fluid as we follow it along its path.) Bernoulli’s principle reinforces the fact that pressure drops as speed increases in a moving fluid: If is greater than in the equation, then must be less than for the equality to hold.
Substituting known values,
Many devices and situations occur in which fluid flows at a constant height and thus can be analyzed with Bernoulli’s principle.
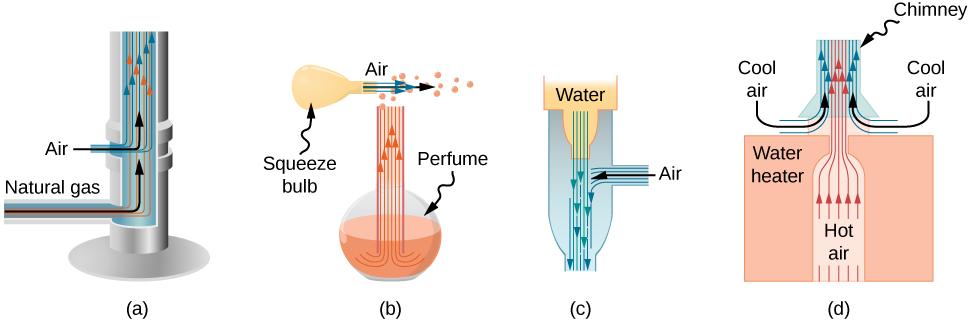
People have long put the Bernoulli principle to work by using reduced pressure in high-velocity fluids to move things about. With a higher pressure on the outside, the high-velocity fluid forces other fluids into the stream. This process is called entrainment . Entrainment devices have been in use since ancient times as pumps to raise water to small heights, as is necessary for draining swamps, fields, or other low-lying areas. Some other devices that use the concept of entrainment are shown in [link] .
[link] shows two devices that apply Bernoulli’s principle to measure fluid velocity. The manometer in part (a) is connected to two tubes that are small enough not to appreciably disturb the flow. The tube facing the oncoming fluid creates a dead spot having zero velocity ( ) in front of it, while fluid passing the other tube has velocity . This means that Bernoulli’s principle as stated in

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?