| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have been avoiding an important issue up to now: When we say that an object moves (more correctly, accelerates) in a way that obeys Newton’s second law, we have been ignoring the fact that all objects are actually made of many constituent particles. A car has an engine, steering wheel, seats, passengers; a football is leather and rubber surrounding air; a brick is made of atoms. There are many different types of particles, and they are generally not distributed uniformly in the object. How do we include these facts into our calculations?
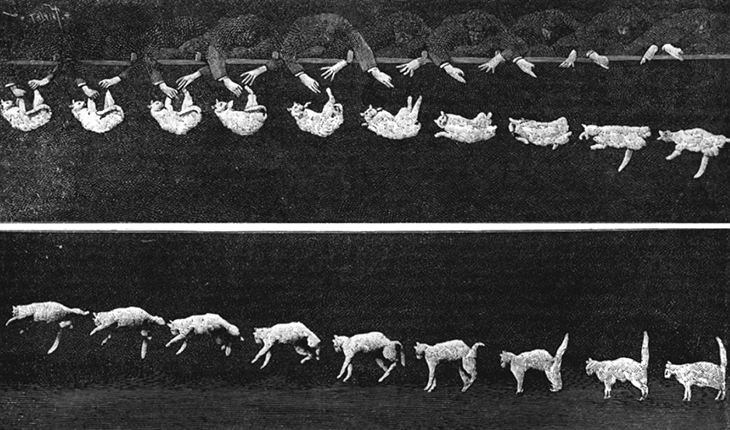
Then too, an extended object might change shape as it moves, such as a water balloon or a cat falling ( [link] ). This implies that the constituent particles are applying internal forces on each other, in addition to the external force that is acting on the object as a whole. We want to be able to handle this, as well.
The problem before us, then, is to determine what part of an extended object is obeying Newton’s second law when an external force is applied and to determine how the motion of the object as a whole is affected by both the internal and external forces.
Be warned: To treat this new situation correctly, we must be rigorous and completely general. We won’t make any assumptions about the nature of the object, or of its constituent particles, or either the internal or external forces. Thus, the arguments will be complex.
Suppose we have an extended object of mass M , made of N interacting particles. Let’s label their masses as , where . Note that
If we apply some net external force on the object, every particle experiences some “share” or some fraction of that external force. Let:
Notice that these fractions of the total force are not necessarily equal; indeed, they virtually never are. (They can be, but they usually aren’t.) In general, therefore,
Next, we assume that each of the particles making up our object can interact (apply forces on) every other particle of the object. We won’t try to guess what kind of forces they are; but since these forces are the result of particles of the object acting on other particles of the same object, we refer to them as internal force s ; thus:
the net internal force that the j th particle experiences from all the other particles that make up the object.
Now, the net force, internal plus external, on the j th particle is the vector sum of these:
where again, this is for all N particles; .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?