| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Recall Newton’s third law: When two objects of masses and interact (meaning that they apply forces on each other), the force that object 2 applies to object 1 is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that object 1 applies on object 2. Let:
Then, in symbols, Newton’s third law says
(Recall that these two forces do not cancel because they are applied to different objects. causes to accelerate, and causes to accelerate.)
Although the magnitudes of the forces on the objects are the same, the accelerations are not, simply because the masses (in general) are different. Therefore, the changes in velocity of each object are different:
However, the products of the mass and the change of velocity are equal (in magnitude):
It’s a good idea, at this point, to make sure you’re clear on the physical meaning of the derivatives in [link] . Because of the interaction, each object ends up getting its velocity changed, by an amount dv . Furthermore, the interaction occurs over a time interval dt , which means that the change of velocities also occurs over dt . This time interval is the same for each object.
Let‘s assume, for the moment, that the masses of the objects do not change during the interaction. (We’ll relax this restriction later.) In that case, we can pull the masses inside the derivatives:
and thus
This says that the rate at which momentum changes is the same for both objects. The masses are different, and the changes of velocity are different, but the rate of change of the product of m and are the same.
Physically, this means that during the interaction of the two objects ( ), both objects have their momentum changed; but those changes are identical in magnitude, though opposite in sign. For example, the momentum of object 1 might increase, which means that the momentum of object 2 decreases by exactly the same amount.
In light of this, let’s re-write [link] in a more suggestive form:
This says that during the interaction, although object 1’s momentum changes, and object 2’s momentum also changes, these two changes cancel each other out, so that the total change of momentum of the two objects together is zero.
Since the total combined momentum of the two objects together never changes, then we could write
from which it follows that
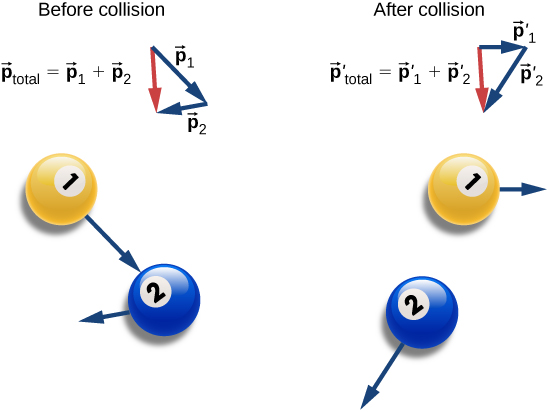
As shown in [link] , the total momentum of the system before and after the collision remains the same.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?